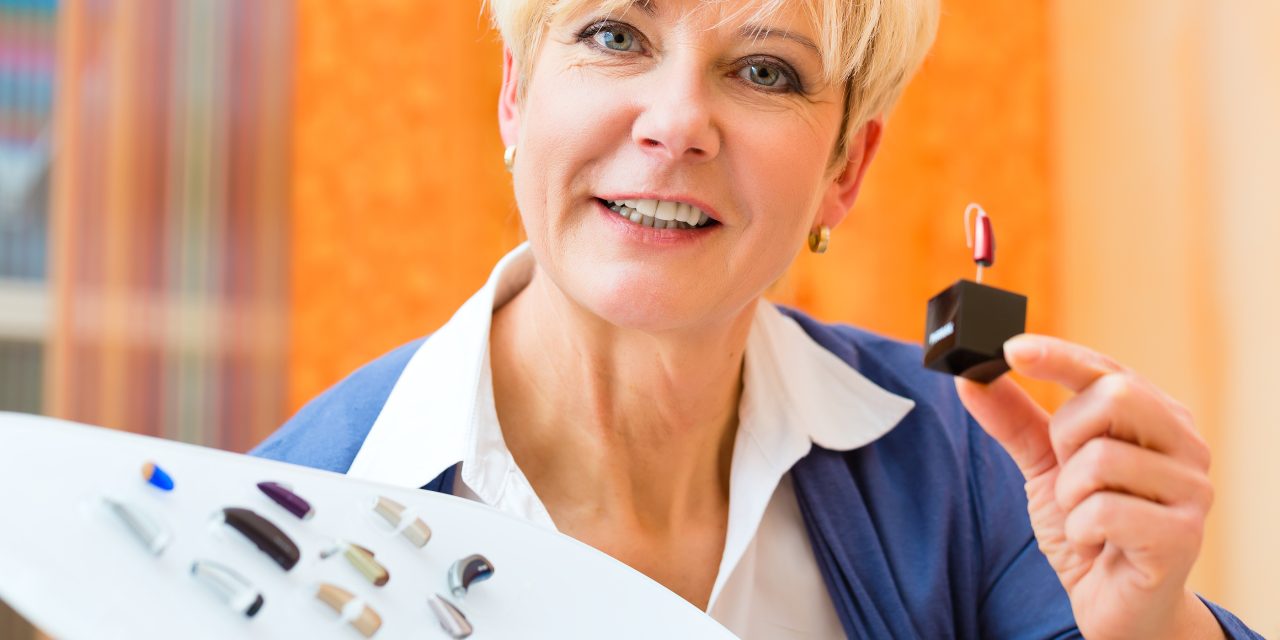
Selecting the best hearing aid for seniors requires careful consideration of individual needs, preferences, and lifestyles. With age, the prevalence of hearing loss increases, presenting a significant barrier to communication and quality of life. The right hearing aid can dramatically improve daily interactions and overall well-being for seniors. It’s important to understand the various types of hearing aids available, along with the features and technology that best serve the senior demographic.

The process of choosing a hearing aid is multifaceted, involving more than just the individual’s hearing loss. Factors such as manual dexterity, visual abilities, and cognitive function must also be considered. In addition, advancements in hearing aid technology have introduced features like wireless connectivity, rechargeable batteries, and tinnitus masking. These features enhance the user’s experience but can also add to the complexity of choosing the most appropriate device. The guidance of a qualified audiologist is essential in navigating the options to find a suitable hearing aid that offers a combination of comfort, clarity, and convenience.
Key Takeaways
- Selecting the right hearing aid involves assessing personal hearing loss and lifestyle needs.
- Modern hearing aids come with advanced features that boost user experience but may require professional guidance.
- The role of audiologists is critical in selecting and fitting the best hearing device for seniors.
Understanding Hearing Loss in Seniors
Hearing loss in seniors is commonly a gradual process that can significantly impact their quality of life. Presbycusis, age-related hearing loss, is the most prevalent type, where individuals may struggle to hear high-frequency sounds or differentiate conversations from background noise.
Factors contributing to hearing loss in seniors include:
- Long-term noise exposure
- Genetics
- Medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure
- Medications that are ototoxic or harmful to the auditory system
The emotional and social effects of hearing loss can be substantial; seniors might experience:
- Social isolation
- Depression
- Anxiety
Seniors should undergo regular hearing screenings, as early detection is crucial for effective management. Hearing aids can greatly improve communication but choosing the right one depends on:
- Degree of hearing loss
- Lifestyle
- Budget
- Manual dexterity
Hearing aids vary from small, in-the-ear models to larger, behind-the-ear devices. Key features seniors might consider include:
- Directional microphones
- Feedback suppression
- Telecoils
- Digital noise reduction
With technological advancements, digital hearing aids have become more prevalent, offering clearer sound quality and connectivity options, like Bluetooth. Proper fitting and customization by a professional is essential for optimal benefit.
Key Features to Consider in Hearing Aids for Seniors
When selecting a hearing aid for seniors, certain features can significantly enhance their listening experience and overall satisfaction. It is important to consider these key attributes to find the most suitable device.
Audio Quality
Audio quality is the most critical aspect of a hearing aid. Devices should provide clear sound and have features like noise reduction and speech enhancement to make understanding easier. Directional microphones are beneficial as they help focus on the sound coming from in front of the user, which is where conversations typically occur.
Comfort and Fit
The comfort and fit of a hearing aid are essential for prolonged daily use. Hearing aids should be lightweight and the correct size to fit the individual’s ear canal comfortably. Custom moldable options may be considered for a personalized fit that does not cause irritation or discomfort.
Ease of Use
Hearing aids should be easy to use for seniors, with features like accessible volume controls and easy-to-change settings. Devices with simple interfaces are preferable, especially for individuals with limited dexterity or vision.
Programmability
Programmability allows hearing aids to be fine-tuned to the user’s specific hearing loss profile. Advanced devices have multiple program settings for different listening environments, such as quiet settings for home use or a program optimized for noisy restaurants.
Connectivity Features
Many modern hearing aids offer connectivity features such as Bluetooth, allowing users to connect to smartphones, televisions, and other devices. This feature can drastically improve the user’s experience by streaming audio directly into the hearing aid.
Battery Life
A long battery life is crucial to minimize the need for frequent changing and ensure the hearing aid is always functional when needed. Devices with rechargeable batteries are convenient and can save the hassle and cost of disposable batteries. It’s also beneficial to consider how battery life may be affected by the use of wireless features.
Types of Hearing Aids
Selecting a hearing aid depends on various factors including the degree of hearing loss, aesthetic preferences, lifestyle needs, and budget. Here are the common types of hearing aids available for seniors.
Behind-The-Ear (BTE)
BTE hearing aids house components in a shell that sits behind the ear, with a clear tube that directs sound into an earmold inside the ear canal. They are suitable for most types of hearing loss and are relatively easy to handle.
In-The-Ear (ITE)
ITE models fill the outer ear. Their larger size allows for additional features like volume control and can accommodate mild to severe hearing loss. However, they are more visible than smaller devices.
In-The-Canal (ITC)
ITC hearing aids are custom molded and fit partly in the ear canal. This style can improve mild to moderate hearing loss and is less noticeable than ITE aids.
Completely-In-Canal (CIC)
CIC devices are almost hidden inside the ear canal. They benefit users with mild to moderate hearing loss who desire a very discreet solution.
Receiver-In-Canal (RIC)
RIC hearing aids are similar to BTE, but they have a tiny wire connecting the receiver directly in the ear canal. This design is often more comfortable and less visible while providing quality sound for a range of hearing losses.
Top Rated Hearing Aids for Seniors
When choosing hearing aids for seniors, one should consider the device’s clarity, comfort, ease of use, and additional features that address the common needs of older adults. Here are three top-rated hearing aids, particularly suitable for seniors:
- Phonak Audeo Paradise: These hearing aids offer excellent sound quality and feature noise-canceling technology. They also provide Bluetooth connectivity, enabling users to easily connect them to smartphones or televisions.
- Type: Receiver-in-canal
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Special Features: Tap control, Motion sensor hearing
- Oticon Opn S: This model prioritizes speech understanding in noisy environments, making them a strong choice for seniors who are socially active. The Oticon Opn S also supports brain health by providing a balanced sound scene.
- Type: Behind-the-ear
- Battery: Disposable or rechargeable options
- Special Features: Tinnitus SoundSupport, OpenSound Navigator
- Starkey Livio AI: Starkey’s Livio AI stands out with integrated sensors and artificial intelligence, offering not only superior sound quality but also tracking of physical activity and cognitive health.
- Type: Various styles available
- Battery: Disposable or rechargeable options
- Special Features: Fall detection, Heart rate monitoring, Language translation
It is important that seniors, or their caregivers, consult with a healthcare professional to select the hearing aid that best fits their specific needs and lifestyle. Technology has come a long way, and many modern hearing aids are designed to be virtually invisible, adding to the wearer’s comfort and confidence.
Insurance and Medicare Considerations
When selecting a hearing aid for seniors, understanding insurance coverage is crucial. Medicare Part A and Part B do not cover hearing aids or exams for fitting hearing aids. However, some Medicare Advantage Plans (Part C) may provide additional benefits, including coverage for hearing aids. Seniors should check the specifics of their Part C plan to determine what is included.
For those with private insurance, coverage varies by insurer and plan. It is vital that they review their policy details or contact their insurance provider to ascertain whether hearing aids are covered and to what extent. Some plans may cover the cost partially or even provide a yearly allowance towards the purchase.
Additionally, seniors can consider Medicaid, which might offer coverage for hearing aids, but this is state-dependent. Requirements and the extent of coverage can vastly differ, so it is recommended to consult the state’s Medicaid program directly.
It’s important to note that some insurers may stipulate:
- A trial period
- Specific hearing aid providers
- Pre-approval processes
Veterans may be eligible for hearing aids through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) if they have hearing loss resulting from their service. They should reach out to the VA for more information.
Lastly, for those without coverage or seeking more affordable options, non-profit organizations and state programs may offer financial assistance or discounts for hearing aids.
Senior citizens are encouraged to thoroughly explore these avenues to help mitigate the costs of hearing aids, as they can be quite significant.
The Role of Audiologists in Selecting Hearing Aids
When seniors seek the ideal hearing aid, the expertise of an audiologist is invaluable. Audiologists assess an individual’s hearing by conducting a comprehensive hearing evaluation. They then use this information to determine the most appropriate type of hearing aid. This process considers several factors:
- Hearing Loss Severity: Audiologists evaluate the degree of hearing loss to recommend an aid with the correct power range.
- Lifestyle Needs: The individual’s daily activities influence the selection of features such as directional microphones or wireless connectivity.
- Manual Dexterity: For users with difficulties handling small objects, audiologists might suggest hearing aids with easy-to-use controls.
The audiologist also looks at the ear’s anatomy to suggest a comfortable fit, whether it’s an in-the-ear or behind-the-ear model. Additionally, they guide the user through the adjustment period, offering advice on usage, maintenance, and acclimatization to the hearing aid.
Audiologists can also help by setting realistic expectations and providing counseling on the implications of auditory health and hearing aids. Long-term support includes regular follow-up appointments to ensure the hearing aid continues to meet the senior’s needs as their situation changes.
Their role doesn’t stop at fitting; audiologists remain a continuous source of support via:
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Fitting | Customizing hearing aid settings to the user’s specific hearing profile. |
| Maintenance | Advising on care and handling to prolong device life. |
| Reprogramming | Adjusting settings as hearing changes or to better suit user preferences. |
| Repairs | Diagnosing and fixing issues or facilitating manufacturer services. |
In essence, audiologists are a crucial ally for seniors in the journey to improved hearing, providing personalized care and advanced technology solutions.
Maintenance and Care of Hearing Aids
Proper maintenance and care are crucial for the longevity and effectiveness of hearing aids. Users should follow a consistent routine to keep their devices in optimal condition.
Daily Cleaning: Hearing aids should be wiped with a soft, dry cloth to remove earwax and moisture. A gentle brush may be used to clean the microphone and speaker areas.
Earwax Removal: Accumulated earwax can block sound output. Users should check for wax build-up daily and use the provided cleaning tools to clear any obstruction.
| Weekly Checks | Action Required |
|---|---|
| Battery Performance | Test and replace batteries as necessary. |
| Tubing and Domes | Inspect for damage or degradation. |
| Sound Quality | Listen for changes in clarity or distortion. |
Moisture Protection:
- Store hearing aids in a dry, cool place.
- Utilize a hearing aid dehumidifier overnight to remove excess moisture.
- Keep them away from steamy bathrooms and extreme temperatures.
Professional Service: Annual check-ups with a hearing care professional ensure that hearing aids are functioning correctly and can help extend their service life.
Battery Safety: Batteries should be stored away from children and pets. Users must dispose of batteries properly, following local regulations, as they may pose environmental hazards when discarded incorrectly.
By adhering to these maintenance guidelines, users can ensure their hearing aids perform well and last longer. Regular care not only maintains sound quality but also prevents costly repairs or replacements.
Assistive Listening Devices and Accessories
Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs) complement hearing aids and cochlear implants, serving to enhance the listening experience in various settings for seniors. There are several types that cater to different needs:
Personal Amplifiers: These are compact devices that amplify sounds closer to the listener while reducing background noise. Suitable for one-on-one conversations, they are especially helpful in quiet environments.
FM Systems: They use radio broadcast technology to transmit sounds directly to the individual’s hearing aid. FM systems are beneficial in classrooms and group meetings where the speaker wears a small microphone linked to the receiver worn by the listener with hearing impairment.
- Infrared Systems: Similar to FM systems but use infrared light to send the audio signal. These are ideal for private settings such as home TVs, as the signal cannot pass through walls.
Induction Loop Systems: Consisting of a loop cable placed around a designated area, they transmit audio signals directly to the hearing aid when it is set to the ‘T’ (telecoil) setting. Commonly found in public venues, like churches and theaters.
Table Microphones: Useful for picking up speech from multiple speakers in meetings or social gatherings. They are often compatible with other ALDs to facilitate better listening experiences.
TV Ears: Specially designed headsets that enhance the audio from televisions. They are wireless, allowing the user to listen at a volume that is comfortable for them without affecting others’ listening levels.
Cost Considerations and Value for Money
When selecting a hearing aid for seniors, cost is a substantial factor. Hearing aids range from $1,000 to $4,000 per unit. The price can increase with advanced features such as wireless technology, noise reduction, and rechargeability.
Seniors should
Innovations and Technological Advancements in Hearing Aids
Recent years have seen significant technological advancements in hearing aids, enhancing the quality of life for seniors with hearing impairment. Digital processing technology has revolutionized hearing aids, allowing for clearer sound with less background noise.
Rechargeable batteries are a notable innovation, eliminating the need for frequent battery replacements. These come with the convenience of wireless charging, similar to that found in smartphones.
Directional microphones have improved considerably, giving users the ability to focus on sounds coming from a specific direction, which helps in understanding speech in noisy environments.
Connectivity features have expanded with Bluetooth integration, allowing hearing aids to connect directly to smartphones, TVs, and other devices. This includes streaming audio directly to the device, making phone calls, and listening to music easier.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Digital Processing | Clear sound, less noise |
| Rechargeable | No frequent battery changes |
| Wireless Charging | Easy charging |
| Directional Mics | Focus on speech |
| Bluetooth | Connect to devices, stream audio |
Many new models boast artificial intelligence (AI), which can learn and adapt to the user’s listening preferences, and some even include health tracking features such as heart rate monitors or fall detection.
Despite these advancements, it’s crucial for seniors to consult with an audiologist to find the most suitable hearing aid for their specific needs, as the efficacy of these features can vary greatly depending on the individual’s hearing loss profile.
Hearing Aid Trial Periods and Warranties
It’s important for seniors to consider trial periods and warranties when selecting a hearing aid. Most manufacturers offer a trial period, typically ranging from 30 to 60 days. During this time, users can assess the device’s comfort, effectiveness, and suitability for their lifestyle. If the hearing aid does not meet their needs, they can return it for a refund or exchange within the trial period.
Warranties are equally crucial as they protect the purchaser against defects and malfunctions. The length and coverage of warranties vary by manufacturer but generally last between one to three years. Some companies may extend the warranty for an additional cost. Here is an outline of what customers typically find in hearing aid warranties:
- Repair Coverage: Covers any necessary repairs not caused by misuse or damage.
- Loss and Damage: Replacement of the hearing aid if lost or damaged, usually subject to a deductible.
Customers should thoroughly understand what the warranty covers. They should also inquire about:
- What components are included in the warranty.
- The process and costs involved in repairs after the warranty expires.
By considering trial periods and warranties, seniors can ensure they find a hearing aid that provides both satisfaction and assurance for their investment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Navigating the many options for hearing aids can be daunting for seniors. This section aims to provide clear answers to common inquiries regarding acquisition, quality, and insurance coverage of hearing aids for seniors.
How can senior citizens obtain hearing aids at no cost?
Seniors with limited income may be eligible for free hearing aids through various non-profit organizations, state programs, or through the Veterans Affairs if they are eligible veterans. Additionally, some manufacturers offer assistance programs for those in need.
What are the highest-rated hearing aids according to Consumer Reports?
Consumer Reports consistently rates behind-the-ear models highly for their balance of quality, comfort, and ease of use. Brands like Phonak, ReSound, and Oticon frequently appear at the top due to their superior sound quality and advanced features.
Which hearing aids are recommended for seniors suffering from dementia?
Hearing aids for seniors with dementia should be user-friendly and have long battery life. Caregiver-friendly features, like remote adjustments via smartphone apps, are also beneficial. Phonak and Oticon offer models that are often recommended for their simplicity and reliability.
Are hearing aids covered for seniors under Medicare insurance plans?
Traditional Medicare does not cover hearing aids or hearing exams for fitting hearing aids. However, some Medicare Advantage plans may offer benefits that include hearing aid coverage. Seniors should check the specifics of their plan for accurate information.
How do Costco hearing aids compare in quality and price for seniors?
Costco offers a range of hearing aids at competitive prices, often including free hearing tests, follow-up appointments, and cleanings. Their in-house brand, Kirkland, is generally well-regarded for quality and value, although selection may be more limited compared to specialized hearing aid providers.
What are the benefits of Oticon and Jabra Enhance hearing aids for seniors?
Oticon hearing aids are known for their BrainHearing technology which supports cognitive health, while Jabra Enhance focuses on seamless connectivity with smart devices and clear sound quality. Both brands offer models that cater to a senior’s usability and comfort, with various levels of customizable features.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting the best hearing aid for seniors involves evaluating various factors such as hearing loss severity, lifestyle preferences, and budget considerations. By exploring the top choices outlined in this guide and consulting with audiologists or hearing healthcare professionals, seniors can make informed decisions that align with their individual needs. Whether opting for behind-the-ear, in-the-ear, or other types of hearing aids, the goal is to improve auditory assistance, enhance communication, and ultimately contribute to an improved quality of life for seniors. It’s essential to prioritize comfort, functionality, and ongoing support to ensure that the selected hearing aid effectively meets the user’s requirements.