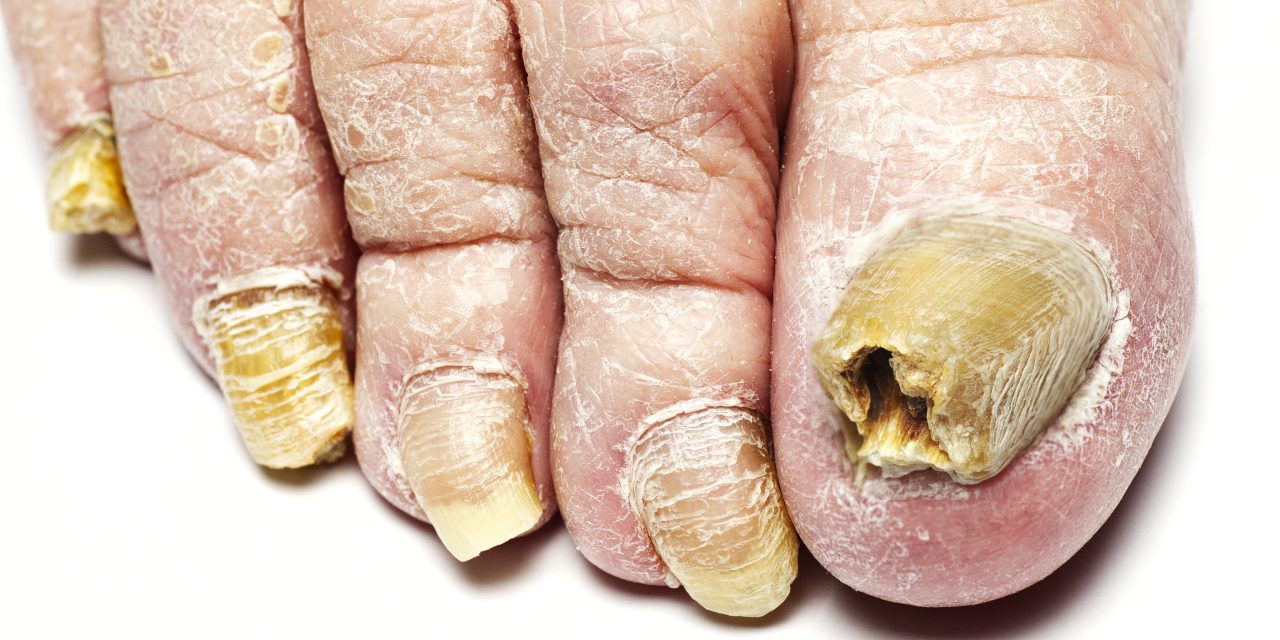
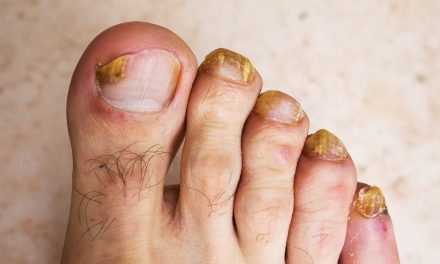
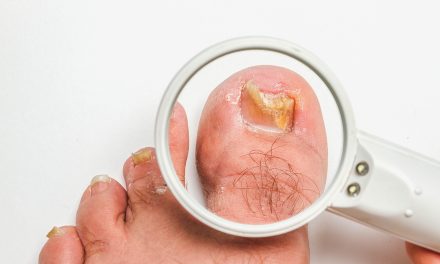
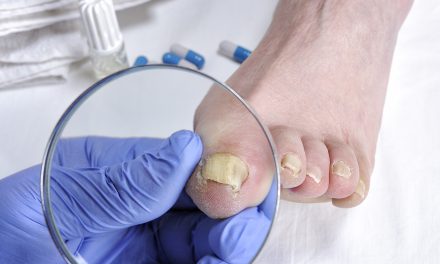
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that can be unsightly and uncomfortable. Many people may be unsure of what toenail fungus actually looks like, as it can present itself in various ways. Early recognition is essential for effective treatment and prevention of this condition.

Typically, toenail fungal infections begin as a small white or yellow spot beneath the tip of the nail. As it progresses, the fungus may cause the nail to change in appearance, becoming thicker, discolored (yellow, brown, or black), and brittle, often having a distorted shape. Eventually, the infected nail could separate from the nail bed, causing discomfort and possible pain.
Key Takeaways
- Toenail fungus often starts as a small white or yellow spot beneath the nail tip
- Infected nails may become thicker, discolored, and brittle as the fungus progresses
- Early recognition of toenail fungus is essential for effective treatment and prevention
Identifying Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus can be both unsightly and a potential health concern. Being able to identify the signs of toenail fungus helps in seeking timely treatment and prevention. This section discusses the key aspects to look out for, such as color changes, nail texture alterations, and nail shape distortion.
Color Changes
Toenail fungus typically causes the affected nail to change color. The most common colors include:
- Yellow: This is the initial stage, where the nail starts to take on a yellowish tint.
- Brown: As the infection progresses, the nail may darken to a brown color.
- White: In some cases, nails may exhibit white patches or streaks.
- Black: Severe cases of toenail fungus may cause the nail to turn black in color.
Nail Texture Alterations
The texture of the infected toenail is likely to change as well. Some observed texture alterations include:
- Thickening: Fungal infection often causes the nail to thicken, making it harder to trim.
- Brittleness: Nails may become crumbly and prone to breaking due to the fungus.
- Ragged: The surface of the nail may become uneven and ragged in appearance.
- Softness: In some cases, the nail can become soft and prone to being indented.
Nail Shape Distortion
Nail shape distortion is another sign of toenail fungus. Key distortions to look out for include:
- Curvature: The nail may become curved or distorted in shape, causing pain or discomfort.
- Separation: Infected nails can sometimes detach from the nail bed, either partially or entirely.
- Ridges: Horizontal or vertical ridges may develop on the surface of the infected nail.
Remember, early detection and treatment of toenail fungus can prevent further complications and lead to a faster recovery. Consult a healthcare professional if you suspect a fungal infection.
Causes of Toenail Fungus
Fungal Organisms
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is typically caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes. The most common culprits include Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton interdigitale, and Epidermophyton floccosum. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can easily infect the toenail area, given the right conditions.
In some cases, non-dermatophyte molds and yeasts can also be responsible for toenail fungus. Candida species, for instance, are more frequently associated with fingernail infections but can occasionally affect toenails as well.
Risk Factors and Susceptibility
Several factors can increase an individual’s susceptibility to toenail fungus. Some of these risk factors include:
- Age: Older adults are more prone to toenail fungus due to slower nail growth and reduced blood circulation.
- Gender: Men are generally more susceptible to toenail fungus compared to women.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can impair the immune system and promote fungal infections.
- Athlete’s foot: The same fungus causing athlete’s foot can spread to toenails, resulting in infections.
- Swimming pools and public showers: Frequently using public swimming pools or showers without protective footwear can expose the nails to fungi.
- Nail injuries: Injuries to the nail or surrounding skin can provide an entry point for fungi.
To help lessen the likelihood of developing toenail fungus, it’s essential to maintain good foot hygiene, wear breathable footwear, and use antifungal treatments as a preventive measure when needed.
Stages of Toenail Fungus
Early Stage Symptoms
In the early stages of toenail fungus, one may notice subtle changes in the appearance of their toenail. The most common signs include:
- Discoloration: The nail may have small white, yellow, or brown spots.
- Thickness: The nail may begin to thicken and grow more slowly.
- Brittle: Nails may become brittle, making them prone to breakage or splitting.
Additionally, one might experience mild discomfort when wearing shoes or walking, as the nail starts to deteriorate.
Advanced Stage Symptoms
As the toenail fungus progresses, the symptoms typically worsen, leading to more noticeable and uncomfortable changes:
- Increased discoloration: The affected nail may darken or develop irregular patches of color.
- Debris build-up: Debris may accumulate under the nail, causing it to separate from the nail bed and emit an unpleasant odor.
- Distorted shape: The nail may become significantly thickened, distorted, or disfigured.
In some cases, the infection can spread to other nails or skin surrounding the affected toenail. Following these stages will help in understanding the severity of the infection and enable one to seek appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options
Topical Medications
Topical medications are an initial treatment option for toenail fungus. These medications are applied directly to the infected nail and surrounding skin. Examples of popular topical antifungal medications include:
- Ciclopirox: an antifungal lacquer that can be applied to the nail.
- Efinaconazole: a topical solution that can effectively reach the nail bed.
It is important to note that topical treatments may require several months of consistent application to see noticeable results. Their effectiveness may vary depending on the severity of the infection.
Oral Antifungal Drugs
Oral antifungal drugs are often prescribed for more severe cases of toenail fungus. Popular options include:
- Terbinafine: a commonly prescribed oral medication that effectively treats most fungal infections.
- Fluconazole: another option that can be used in cases where terbinafine is not suitable.
These medications are typically prescribed for periods of 3 to 6 months. They work by promoting healthy nail growth and gradually replacing the infected nail. However, potential side effects like liver dysfunction and drug interactions should be monitored closely.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a relatively new treatment for toenail fungus. It uses targeted light energy to heat and destroy the fungal cells within the nail. This treatment option may be recommended for patients who have not seen success with topical or oral treatments. Some benefits of laser therapy include:
- Quick treatment times: Individual sessions typically last between 20 to 30 minutes.
- No known major side effects: Laser therapy is considered to be a safe and non-invasive treatment option.
It is important to keep in mind that, although promising, laser therapy may not be covered by insurance and can be more expensive than other treatment options.
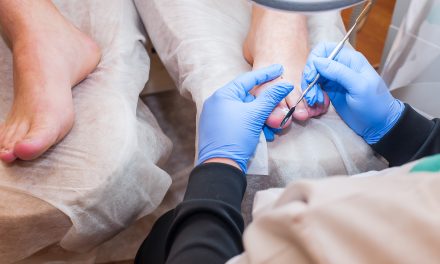
Surgical Removal
In extreme cases, surgical removal of the infected nail may be necessary. This involves removing the entire nail or part of the nail, as well as any infected tissue underneath. While this method can be effective in treating severe infections, it is typically reserved for cases where other treatments have failed, or when pain and discomfort are too severe.
Surgical removal is performed by a healthcare professional and can result in longer healing times. It is essential to follow all post-operative care instructions provided by the healthcare provider to ensure proper healing and reduce the risk of complications.
Preventing Toenail Fungus
Foot Hygiene Practices
Practicing proper foot hygiene is crucial to prevent toenail fungus. Here are some steps to follow:
- Wash feet daily: Use warm water and mild soap to clean feet, paying close attention to the spaces between the toes. Dry your feet thoroughly to avoid a moist environment that encourages fungal growth.
- Trim nails regularly: Keep toenails trimmed straight across with clean nail clippers. Avoid cutting too close to the skin or rounding the toenail edges, as doing so can cause ingrown toenails.
- Apply antifungal powder: If you’re prone to fungal infections, use antifungal powder on your feet and inside your shoes to help keep the fungus at bay.
Proper Footwear Choices
It’s also crucial to choose the right footwear to prevent toenail fungus. Consider the following tips for optimal foot health:
- Opt for breathable shoes: Look for shoes made of materials like leather, canvas, or mesh which allow for air circulation, reducing the buildup of moisture that can lead to fungal growth.
- Wear moisture-wicking socks: Socks made of synthetic materials, such as polyester or nylon, are designed to wick moisture away from the feet, keeping them dry and less susceptible to fungal infection.
- Choose proper-fitting shoes: Shoes that are too tight can cause toenail trauma, and those that are too loose can create friction between your feet and the shoes. Both situations can invite fungal infections.
- Rotate your shoes: Allow your shoes to air out properly after wearing them by switching out your footwear every day. This aids in keeping your shoes dry and fungus-free.
- Protect your feet in public areas: When in communal areas like gyms or swimming pools, wear flip-flops or shower shoes to avoid direct contact with the floor, which could expose feet to fungal infections.
By following proper foot hygiene practices and choosing appropriate footwear, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing toenail fungus and maintain healthy toenails.
Complications of Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus may seem like a minor cosmetic issue, but if left untreated, it can lead to more severe complications. In this section, we’ll discuss two potential consequences: secondary infections and the spread of the fungus to other nails.
Secondary Infections
If a toenail fungus infection is not treated promptly, it can create an environment where bacteria can thrive. This may result in a secondary bacterial infection that can cause additional pain, swelling, and redness around the affected toe. In more severe cases, this bacterial infection can spread to the skin surrounding the nail, a condition known as cellulitis.
At-risk groups for developing cellulitis include those with compromised immune systems, diabetes, or poor circulation. When left untreated, cellulitis can be dangerous and may even lead to hospitalization. Thus, it’s crucial to address toenail fungus promptly to minimize the risk of secondary infections.
Spread to Other Nails
Another complication of toenail fungus is its ability to spread to nearby nails. It can transfer to other toenails, as well as the fingernails, causing more extensive damage.
Here are some ways to prevent the spread of toenail fungus:
- Keep the affected nails clean and dry. Moist environments promote fungal growth.
- Do not share personal items like nail clippers or files.
- Wear shoes and socks that ‘breathe’ and help to reduce moisture.
- Avoid walking barefoot in public areas where the fungus can be contracted, such as gyms, saunas, and swimming pools.
By keeping toenails clean, dry, and properly treating a present fungal infection, the risk of the fungus spreading to other nails can be minimized. Addressing a toenail fungus infection promptly is essential to prevent these complications and maintain overall foot health.
Diagnosis of Toenail Fungus
Physical Examination
During the physical examination, a healthcare professional will carefully inspect the affected toenail(s) for signs of a fungal infection. Common visual indicators of toenail fungus include:
- Discoloration (yellow, brown, or white)
- Thickening of the nail
- Brittleness or crumbling edges
- Distorted nail shape
- Odor coming from the infected nail
In some cases, the healthcare professional might use a magnifying glass or a dermatoscope to get a closer look at the nail. It is essential to differentiate toenail fungus from other conditions like psoriasis, nail trauma, or onychogryphosis, which may share similar symptoms.
Laboratory Testing
If the physical examination is not conclusive, further laboratory testing might be necessary for an accurate diagnosis. The most common lab tests for toenail fungus are:
- KOH test: A small scraping from the affected nail is placed in a potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution, which dissolves non-fungal elements and allows for microscopic examination of the remaining sample.
- Fungal culture: The collected nail sample is placed in a culture medium to promote the growth of fungi, which may take several weeks. It helps identify the specific fungal species causing the infection.
- PAS staining: A periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining can highlight the presence of fungal elements in the nail material, which may not be visible with the KOH test alone.
- PCR test: A relatively new, highly sensitive, and rapid method for diagnosing toenail fungus is the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test. It can identify fungal DNA in nail samples and distinguish between various fungal species.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the most effective treatment plan for toenail fungus. Healthcare professionals rely on a combination of physical examination and laboratory testing methods, ensuring a comprehensive assessment.
Home Remedies
When dealing with toenail fungus, there are various home remedies that one can try. These remedies are generally divided into two main categories: natural oils and vinegars, and over-the-counter treatments.
Natural Oils and Vinegars
Tea tree oil is a popular natural remedy for toenail fungus. Dilute the oil with a carrier oil, such as olive or coconut oil, and apply it to the infected area twice daily for a few weeks. This oil has antifungal and antibacterial properties that help combat the fungus.
Apple cider vinegar can also be effective in treating toenail fungus. Mix equal parts vinegar and water in a bowl or tub, and then soak the affected foot in the solution for approximately 30 minutes daily. The acidity of the vinegar helps to eliminate the fungus.
Another natural treatment for toenail fungus is oregano oil. This oil has antifungal properties and can be mixed with a carrier oil before being applied to the affected area twice daily.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
There are also over-the-counter (OTC) options available for treating toenail fungus. Some of these treatments include:
- Antifungal creams: Apply the cream directly to the infected toenail as directed by the product’s instructions. These creams often contain active ingredients like terbinafine or clotrimazole, which help to eliminate the fungus. Examples of OTC antifungal creams include Lamisil and Lotrimin.
- Antifungal nail polishes: These polishes, such as Penlac and Dr. Remedy, contain antifungal ingredients and can be applied to the affected toenail. They’re usually applied once daily for a few weeks to help clear the infection.
- Antifungal foot powders: Foot powders, such as Zeasorb and Ting, can be sprinkled inside shoes and socks to help keep the feet dry and discourage fungal growth.
While home remedies can sometimes be helpful in treating toenail fungus, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional if the infection is severe or does not improve. They may recommend prescription medications or other treatments to effectively combat the fungus.
When to See a Doctor
Signs of Severe Infection
It is essential to consult a doctor if you notice intense pain, redness, or swelling around the affected toenail. Additionally, if you experience fever, pus, or an unpleasant odor emanating from the toe, these could be indicators of a severe infection. In such cases, medical attention should be sought immediately to prevent further complications.
Lack of Improvement
If your toenail fungus shows no signs of improvement even after using over-the-counter treatments and maintaining proper foot hygiene for several weeks, it’s time to see a doctor. A healthcare professional can provide a more accurate diagnosis and recommend alternative treatment options, such as:
- Prescription medications: oral antifungal drugs or topical treatments.
- Nail removal: in severe cases, the doctor may suggest removing the infected nail to allow a new, healthy nail to grow.
- Laser therapy: a less invasive option that uses light energy to eliminate the fungus.
Remember, it’s better to seek medical advice early on to prevent the infection from worsening and spreading to other nails or people around you.
Long-Term Management
Routine Nail Care
Practicing proper nail care is essential to prevent the recurrence of toenail fungus. To ensure healthy nails, follow these steps:
- Trim nails regularly, keeping them straight across and slightly rounded at the tips.
- Clean nails with gentle soap and water, and make sure to dry them thoroughly.
- Moisturize nails with a nourishing nail oil.
- Wear breathable socks and shoes to prevent a moist environment.
- Disinfect any instruments used on the nails, such as clippers and files.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| Trim | Cut nails straight across and rounded at the tips. |
| Clean | Use gentle soap and water; dry thoroughly. |
| Moisturize | Apply nourishing nail oil. |
| Breathable footwear | Choose socks and shoes that allow air circulation. |
| Disinfect | Sanitize nail clippers and files after each use. |
Monitoring for Recurrence
It is crucial to monitor for the early signs of fungal recurrence, as early detection allows for prompt treatment. Watch for the following indications of toenail fungus:
- Discoloration of the nail, such as yellowing or darkening
- Thickening or distortion of the nail
- Separation of the nail from its nail bed
- Formation of white or yellow streaks on the nail
- Unpleasant odor emanating from the affected nail
If any of these signs are observed, consult a healthcare professional for advice on the necessary treatment. By maintaining a vigilant routine of nail care and monitoring, individuals can effectively manage toenail fungus in the long term.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the signs of toenail fungus infection?
Toenail fungus infections, also known as onychomycosis, often begin as a small white or yellow spot beneath the tip of the toenail. As the infection progresses, the following symptoms may develop:
- Thickening of the nail
- Discoloration, turning yellow, brown, or black
- Distortion or changes in shape
- Brittleness, crumbling, or splitting of the nail
- Foul-smelling buildup beneath the nail
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area
What are the effective treatments to combat toenail fungus?
There are several treatments for toenail fungus, ranging from over-the-counter (OTC) remedies to prescription medications:
- OTC antifungal creams and ointments applied directly to the affected nail
- Prescription topical antifungal medications, such as ciclopirox or efinaconazole
- Oral antifungal drugs, like terbinafine, itraconazole, or fluconazole
- Nail lacquers containing antifungal ingredients applied like polish
- In more severe cases, removal of the infected nail may be necessary.
Consult a healthcare professional for the most suitable treatment.
Can toenail fungus resolve on its own, and how can you tell?
In some cases, mild toenail fungus may resolve without treatment. However, this is rare. Improvement in hygiene, keeping the feet dry, and proper nail care can sometimes help. To confirm the resolution of a toenail fungus infection, the nail should return to its normal color, shape, and consistency without any signs of active infection.
What factors contribute to the development of toenail fungus?
Several factors increase the risk of developing toenail fungus:
- Aging, due to decreased blood circulation and slower nail growth
- A humid environment, such as public showers, swimming pools, or locker rooms
- Sweaty feet, tight shoes, or synthetic socks that trap moisture
- Trauma or injury to the nail
- Preexisting medical conditions, such as diabetes or a weakened immune system
What are the common misdiagnoses when identifying toenail fungus?
Toenail fungus might be mistaken for other nail conditions, such as:
- Psoriasis, an autoimmune skin condition that can cause changes in nail appearance similar to those of a fungal infection
- Nail trauma, which can result in discoloration and thickening
- Bacterial infections, which can cause inflammation and discoloration of the nail
A healthcare professional can confirm a toenail fungus diagnosis by analyzing a nail sample under a microscope or testing it in a laboratory.
How can toenail fungus be differentiated from other nail conditions?
To differentiate toenail fungus from other nail conditions, a healthcare professional may perform the following tests:
- KOH test: A potassium hydroxide solution is applied to a nail sample, which dissolves keratin to reveal fungal hyphae under the microscope
- Fungal culture: A nail sample is placed in a culture medium to grow and identify the specific fungus involved
- Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining: A nail sample is treated with specific chemicals and examined under a microscope to identify fungal elements
These tests can help determine if the nail condition is fungal or non-fungal in nature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing the signs and symptoms of toenail fungus is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective management. Understanding the visual characteristics, such as discoloration, thickening, and changes in nail texture, can aid in identifying toenail fungus. Seeking timely medical evaluation and exploring appropriate treatment options are essential for addressing toenail fungus and preventing its progression. Additionally, practicing good foot hygiene, wearing breathable footwear, and taking preventive measures can contribute to overall foot health and reduce the risk of toenail fungus. By being attentive to the appearance of the nails and seeking appropriate care, individuals can work towards maintaining healthy nails and overall foot wellness.