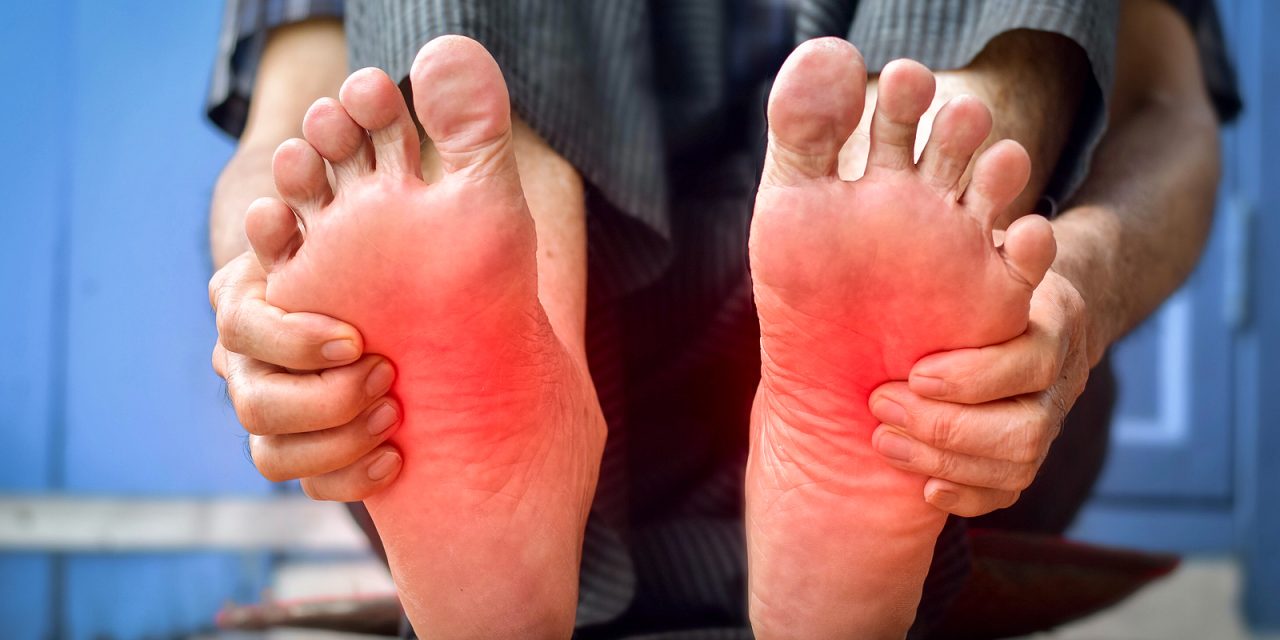
Neuropathy in the feet is a condition that often causes numbness, tingling, and pain. While it’s commonly associated with diabetes, it can also result from injuries, infections, and exposure to toxins or be inherited. Patients seeking relief from these troubling symptoms have various treatment options at their disposal. Depending on the underlying cause, current medical treatments aim to slow the progression, manage symptoms, and if possible, cure the neuropathy.
Due to the complexity of this condition, treatments range from medications and therapy to lifestyle changes and home remedies. Finding an effective treatment can be a journey of trial and error, but advancements in medical research continue to provide hope for those affected. Health practitioners may prescribe a combination of therapies to achieve the best results, which often includes controlling blood sugar levels, taking medications, engaging in physical therapy, and using assistive devices.
Key Takeaways
- Neuropathy in the feet causes symptoms like numbness and pain, often requiring a combination of treatments.
- Management can include medication, therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and alternative remedies.
- Ongoing research aims to optimize treatment plans and improve the quality of life for those with neuropathy.
Understanding Neuropathy
Neuropathy encompasses a range of conditions caused by nerve damage, particularly in the peripheral nervous system. Accurate diagnosis is pivotal, often necessitating a comprehensive medical history and a combination of tests.
Types of Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is a common type impacting the nervous system outside of the brain and spinal cord. It includes multiple categories, such as:
- Mononeuropathy: Damage to a single peripheral nerve.
- Polyneuropathy: Involves several nerves, often with similar symptoms across affected areas.
- Autonomic Neuropathy: Affects the nerves that control involuntary bodily functions.
Each type influences the nervous system distinctly, warranting a tailored approach for diagnosis and management.
Common Causes of Neuropathy
Neuropathy can result from a multitude of factors. Some prevalent causes include:
- Diabetes: The leading cause of peripheral neuropathy, where high blood sugar levels damage nerves.
- Infections: Certain viral or bacterial infections can lead to neuropathic conditions.
- Autoimmune diseases: Diseases where the immune system mistakenly attacks nerves.
Other causes involve hereditary conditions, trauma, and exposure to toxins.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Neuropathy symptoms often include tingling, numbness, pain, and weakness in the affected area. Diagnosis typically begins with a neurologist reviewing the patient’s medical history, followed by:
- Physical and neurological examinations: To check for muscle weakness, tendon reflexes, and sensory deficits.
- Blood tests can uncover vitamin deficiencies, diabetes, and other potential causes.
- Skin biopsy: This procedure may look at nerve fiber endings and assess nerve damage.
Comprehensive diagnostic evaluations help to ascertain the presence and extent of neuropathy and guide subsequent treatment options.
Medical Treatments for Neuropathy
When it comes to neuropathy in the feet, medical treatment options vary based on the underlying cause and the severity of nerve pain. Prescription medications are often at the forefront, with both oral and topical treatments available to manage symptoms. Some medications can cause side effects, so it is important for patients to discuss the benefits and potential risks with their healthcare provider.
Prescription Medications
Prescription medications used to treat neuropathy in the feet include anticonvulsants and antidepressants, which can help to manage nerve pain. Common choices are:
- Anticonvulsants: Gabapentin and pregabalin are frequently prescribed to reduce nerve pain by stabilizing electrical activity in the nerves.
- Antidepressants: Medications such as duloxetine and amitriptyline may be used for pain relief even in individuals not suffering from depression.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs: Mexiletine, related to lidocaine, is sometimes used to treat neuropathy pain.
Patients should be aware that these medications can have side effects ranging from dizziness to fatigue, which should be monitored by a healthcare provider.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
For mild neuropathy pain, over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers may be recommended. These include:
- Anti-inflammatories: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- People should use OTC medications with caution, as long-term use can lead to other health issues such as gastrointestinal problems.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments offer localized relief from the nerve pain associated with neuropathy. These include:
- Capsaicin: Derived from chili peppers, capsaicin cream can, when applied to the skin, provide pain relief by reducing the amount of substance P, a chemical involved in transmitting pain signals.
- The effectiveness and side effects, which can include burning or irritation at the application site, may vary among individuals.
Each treatment may work differently for each individual, and it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate approach.
Non-Pharmacological Therapies
Non-pharmacological therapies for neuropathy in feet focus on alleviating symptoms without medication. These therapies may improve physical function, reduce pain, and enhance balance through various techniques.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy aims to strengthen muscles, improve movement, and increase stability. A physical therapist may design a personalized exercise program that targets the specific needs of a patient with foot neuropathy. Exercises can include range-of-motion exercises, stretching, and low-impact activities like swimming or cycling that foster muscle strength and improve balance.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medical practice that involves the insertion of thin needles into the skin at specific points on the body. It can help manage pain and improve nerve function in patients with neuropathy. Acupuncture stimulates the body’s natural healing processes and is considered a safe and beneficial adjunct therapy for neuropathic pain.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) uses a battery-powered device to deliver low-voltage electrical currents through the skin via electrodes. The therapy is believed to reduce pain by interrupting pain signals to the brain and by stimulating the production of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers. TENS is a non-invasive, self-administered therapy that can be tailored to fit the individual’s level of neuropathic pain.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in managing neuropathy in the feet. By adjusting diet and nutrition, managing blood sugar levels, and committing to smoking and alcohol cessation, individuals can significantly impact the progression and symptoms of this condition.
Diet and Nutrition
Adopting a diet that is rich in essential vitamins and nutrients can be beneficial for those suffering from neuropathy. This includes a high intake of leafy green vegetables and lean proteins, as well as complex carbohydrates that help to maintain a steady level of blood sugar.
Key Dietary Components:
- Vitamins B12 and D: Essential for nerve health.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Help reduce inflammation.
- Antioxidants: Found in fruits and vegetables, help protect nerve cells.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Keeping blood sugar levels within a normal range is crucial for people with diabetic neuropathy. Consistent management can slow the progression of neuropathy.
Steps to Manage Blood Glucose:
- Regularly monitor blood glucose levels.
- Follow a balanced meal plan designed to stabilize blood sugar.
Smoking and Alcohol Cessation
Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake are important steps in managing neuropathy. Smoking constricts blood vessels and worsens blood flow to the extremities, exacerbating neuropathic symptoms.
Benefits of Cessation:
- Quit Smoking: Improves circulation, supporting nerve health.
- Limit Alcohol: Heavy alcohol use can cause and worsen neuropathy.
Natural and Alternative Remedies
Natural and alternative remedies for neuropathy in feet may provide relief for symptoms like pain and tingling. These remedies include specific supplements and vitamins, the use of essential oils and herbal treatments, as well as simple home practices.
Supplements and Vitamins
Supplements such as alpha-lipoic acid can be a beneficial addition to managing symptoms of neuropathy. Alpha-lipoic acid is an antioxidant that may help improve nerve function and relieve symptoms like pain and tingling. Vitamin D supplementation might also play a role; research suggests that maintaining adequate levels of vitamin D can support nerve health.
- Supplements to consider:
- Alpha-lipoic acid
- Vitamin D
Essential Oils and Herbal Treatments
Using essential oils, like lavender or peppermint, might offer temporary relief when massaged into the feet, though evidence is mostly anecdotal. Moreover, certain herbal treatments have been recognized for their potential to alleviate nerve pain. For example, the application of Artemisia can be considered for its pain-relieving properties. Always consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any new treatment regimen to ensure it’s safe for your individual health needs.
- Herbs and oils that may help:
- Lavender oil
- Peppermint oil
Home Remedies
Home remedies such as Epsom salt foot soaks can help soothe aching feet and may improve circulation, which can be beneficial for those with neuropathy. It is important to use warm, not hot, water to avoid burns, especially since neuropathy might dull the ability to sense temperature changes. Walking regularly helps improve blood flow, which can nourish damaged nerves and potentially reduce symptoms.
- Simple actions to take at home:
- Epsom salt foot soaks
- Regular walking or gentle exercises
Prevention and Management of Neuropathy
Managing neuropathy effectively involves a proactive approach to prevention, especially of injuries, and stress management through lifestyle changes. Engaging in preventative measures and integrating stress-reducing practices like meditation can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Injury Prevention
Preventing injuries to the feet is crucial for individuals with neuropathy, as they might not feel pain from wounds due to decreased sensation. Patients should:
- Inspect feet daily: Check for cuts, blisters, or signs of injury.
- Wear well-fitting shoes: This protects the feet and reduces the risk of skin breakdown or deformities.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can exacerbate neuropathic pain. To manage stress, individuals can:
- Adopt healthy lifestyle changes: Regular exercise and a balanced diet can have positive effects on overall stress levels.
- Practise meditation: This method of relaxation can help reduce the body’s stress response and manage the discomfort associated with neuropathy.
Special Considerations in Neuropathy
Neuropathy, or nerve damage in the feet, varies based on its underlying cause, which necessitates tailored approaches to treatment and management. Each type of neuropathy may have distinct triggers such as diabetes, chemotherapy, or age-related factors, carrying specific considerations for an effective cure.
Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy results from prolonged high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes, leading to nerve damage in the feet. Managing blood glucose is critical to prevent further damage and alleviate symptoms. For those with existing complications, a multifaceted approach that may include blood sugar control, medication, and lifestyle modifications, is often recommended. In severe cases, amputation may be warranted to prevent the spread of infection.
Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathy
Chemotherapy treatments can cause neuropathy as a side effect, due to the toxic effects of the drugs used on nerve tissues. Patients undergoing chemotherapy require routine monitoring, and the management of symptoms often involves the use of medications. Adjusting the chemotherapy regimen may be necessary if neuropathy becomes severe. Supportive therapies and supplements are also explored to help ease the symptoms.
Neuropathy in the Elderly
Elderly individuals often deal with neuropathy due to a range of causes, such as age-related decline and disorders like Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Treatment in the elderly must consider potential interactions with other medications and the increased risk of falls due to impaired sensation. Proactive foot care and regular monitoring are necessary to prevent complications like ulcers, which could lead to infection and possibly amputation.
Supportive Devices and Aids
Individuals with neuropathy in their feet often benefit from specific devices and aids designed to provide support and alleviate discomfort.
Specialized Footwear
Specialized footwear can make a significant difference for people suffering from neuropathy. Shoes designed for neuropathy are often wider and deeper to accommodate swollen feet or custom orthotics. They tend to have extra padding and non-binding uppers, providing essential support without restricting circulation. It is crucial to choose shoes with smooth interiors that minimize friction against the feet, which can agitate sensitive nails and skin.
Diabetic socks are another key part of footwear for neuropathy. These socks are typically non-elasticated to prevent constriction and are made from moisture-wicking materials to maintain a dry environment, reducing the risk of foot ulcers.
Braces and Orthotics
Braces and orthotics offer structural support, improve foot alignment, and distribute pressure more evenly. Custom orthotics are particularly helpful because they are molded to the contours of the individual’s feet, ensuring an exact fit that accommodates any irregularities.
For those with significant foot drop or other muscular challenges due to neuropathy, ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs) can be a beneficial intervention. These braces support the ankle and hold the foot in a proper position, which aids in walking and stability.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
Neuropathy in the feet can lead to symptoms such as pain, tingling, and numbness. These sensations might indicate nerve damage, which requires medical attention to manage and prevent further complications.
Seeking Medical Advice
Patients should consult a healthcare provider when they experience persistent symptoms of neuropathy, including:
- Persistent Pain: Ongoing discomfort in the feet that does not improve over time.
- Tingling or Numbness: These sensations, particularly when they are chronic or worsening, may suggest nerve damage.
- Unusual Symptoms: Dizziness, headaches, constipation, or other signs that seem unrelated to the feet may actually be linked to systemic nerve damage.
- Discomfort Impacting Daily Life: When symptoms interfere with daily activities or sleep patterns, it’s important to seek professional advice.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To maximize the effectiveness of the healthcare appointment, patients should:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a detailed record of all symptoms, regardless of whether they seem related, including onset, duration, and severity.
- List All Medications: Compile a list of medications, supplements, and dosages currently being taken.
- Note Medical History: Include any previous health issues or treatments that could be linked to neuropathy.
- Ask About Tests: Be prepared to inquire about diagnostic tests, such as blood work or nerve function tests, which may be suggested by the Mayo Clinic to evaluate neuropathy.
Each of these steps will aid the doctor in making an accurate diagnosis and developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Navigating Treatment Options
The journey to mitigate neuropathy in feet involves understanding the effectiveness of various therapies and managing potential side effects. Patients may encounter a range of treatments from medication to lifestyle changes aimed at reducing nerve pain and improving quality of life.
Understanding Treatment Efficacy
When addressing neuropathic pain, particularly the sensation of burning or tingling in the feet, it is essential to consider treatment efficacy. Medication is a common approach, with options like duloxetine (Cymbalta) showing promise in controlling nerve pain. Additionally, therapies such as regular exercise, including walking, may enhance blood flow and nourish damaged nerves. However, not all treatments are equally effective; certain drugs, like pregabalin, have been reported as less effective in some studies.
Some conditions causing neuropathy, like nerve compression, may be reversible with surgery. However, most neuropathic pain is chronic and treatments aim to manage symptoms rather than cure the underlying condition.
Dealing with Side Effects and Complications
All treatments come with the potential for side effects, and it’s crucial for patients to be aware of these risks. Antidepressants, for instance, may offer pain relief but could also lead to a variety of side effects from drowsiness to dry mouth. The Harvard Health Blog highlights that while nortriptyline may have a higher rate of side effects, mexiletine tends to have fewer, though no serious side effects were reported in the study examined.
Patients and healthcare professionals must weigh the benefits of alleviating neuropathic pain against the risk of side effects, which can sometimes lead to medication tolerance. This emphasizes the importance of a tailored treatment plan that is closely monitored for both efficacy and tolerability.
Future of Neuropathy Treatment
The landscape of neuropathy treatment is evolving as new research sheds light on potential therapies and the complex nature of nerve damage. Key advancements include targeted medicines and lifestyle interventions to enhance nerve regeneration and relieve symptoms.
Research and Developments
Scientists are rigorously studying the mechanisms underlying neuropathic pain to discover more effective treatments. Imaging techniques are improving, enabling researchers to observe nerve damage in greater detail and understand its progression. These advancements in imaging are pivotal for the development of more effective therapies. Research suggests that nerve damage related to alcoholism and alcohol abuse may be reversible if detected early, emphasizing the importance of precise imaging and early intervention.
Emerging Therapies
The pipeline for new neuropathy treatments includes promising drugs aimed at different aspects of the disease. One such drug, mentioned in recent news, has shown it may effectively treat chronic neuropathic pain, a condition often resistant to current first-line therapies like gabapentin and duloxetine. Furthermore, treatment strategies focusing on lifestyle changes—specifically, diet and exercise—are gaining attention for their role in improving blood flow and potentially aiding nerve regeneration, as highlighted by studies suggesting non-drug approaches can immediately benefit many people with peripheral neuropathy. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on blood pressure management as a part of comprehensive neuropathy care, considering the impact of vascular health on nerve function.
Frequently Asked Questions
The search for remedies for neuropathy in the feet often leads to a blend of self-care practices and medical treatments. The following frequently asked questions encapsulate the spectrum of ways one may approach managing this condition.
How can one reverse neuropathy in the feet effectively?
One cannot typically reverse neuropathy in the feet thoroughly, but managing the underlying cause and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits can improve symptoms. Regular exercise and blood sugar control are paramount for those with diabetic neuropathy.
Which home remedies are effective for treating neuropathy in the legs and feet?
Home remedies that may provide relief include regular walking or exercises approved by a healthcare provider. Additionally, using foot soaks and maintaining good foot health is advisable to alleviate discomfort.
What are the most successful medical treatments available for neuropathy?
The most successful medical treatments for neuropathy often include medications for pain relief, such as nortriptyline, which has shown a significant improvement in discomfort for some patients. Regular consultation with healthcare providers is essential for tailor-fitting the treatment plan.
What symptoms indicate the presence of neuropathy in feet?
Neuropathy symptoms in the feet can include tingling, numbness, sharp pains, sensitivity to touch, and muscle weakness. Persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional for diagnosis and guidance.
Are there any particular triggers that can worsen neuropathy in feet?
Triggers that can exacerbate neuropathy symptoms include poor glycemic control in diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, excessive alcohol consumption, exposure to toxins, and certain medications. Individuals should consult healthcare providers to identify and manage personal triggers.
How can the progression of peripheral neuropathy be halted or slowed down?
Progression of peripheral neuropathy can often be slowed down by addressing the underlying cause, such as improved management of diabetes or nutritional interventions. Close monitoring by healthcare professionals and compliance with treatment regimens are crucial steps for hindering disease progression.