Fungal toenail infections can be more than just a cosmetic concern; they can also cause discomfort and lead to more serious issues if not treated properly.
It’s a common problem that many people face, often without knowing the most effective ways to address it.
To effectively get rid of a fungal toenail infection, persistent treatment using topical or oral antifungal medications is crucial. These treatments can take time, sometimes even several months, to show results.
There are also natural remedies that some people find helpful, such as tea tree oil or olive leaf extract, which may support the reduction of fungal growth.
Individuals with certain health conditions, like diabetes, should consult a healthcare provider before starting any treatment plan.
Consistently following preventive measures can help avoid future infections, such as keeping feet dry and changing socks regularly.
Key Takeaways
- Persistent use of antifungal treatments is crucial.
- Natural remedies may complement medical treatments.
- Prevention is key to avoiding future infections.
Understanding Toenail Fungal Infections
Toenail fungal infections, also known as onychomycosis, involve discoloration and thickening of the nails. Left untreated, these infections can lead to complications that impact nail texture and comfort.
What Is Onychomycosis?
Onychomycosis is a common type of nail fungus that primarily affects toenails. It occurs when fungi enter the nail bed, often through tiny cuts in the skin surrounding the nail or through cracks in the nail itself.
The fungi thrive in warm, moist environments such as shoes or communal showers.
Toenails are affected more often than fingernails. This is because feet are often confined in a warm, moist environment inside shoes, which encourages fungal growth. Treatment can be challenging and may require both topical and oral antifungal medications.
Symptoms and Complications
A fungal infection in the toenail typically presents as discoloration. The nail may turn white, yellow, or brown.
Over time, the nail can become thick, brittle, and crumbly. It may also lift from the nail bed, causing discomfort.
If the infection is not treated, the symptoms can lead to further complications. These include pain during walking or standing, and a noticeable odor.
In severe cases, the infection may spread to other toenails or skin, potentially leading to athlete’s foot or even bacterial infections in the surrounding area.
Individuals with diabetes or compromised immune systems should be particularly cautious, as complications can be more severe for them.
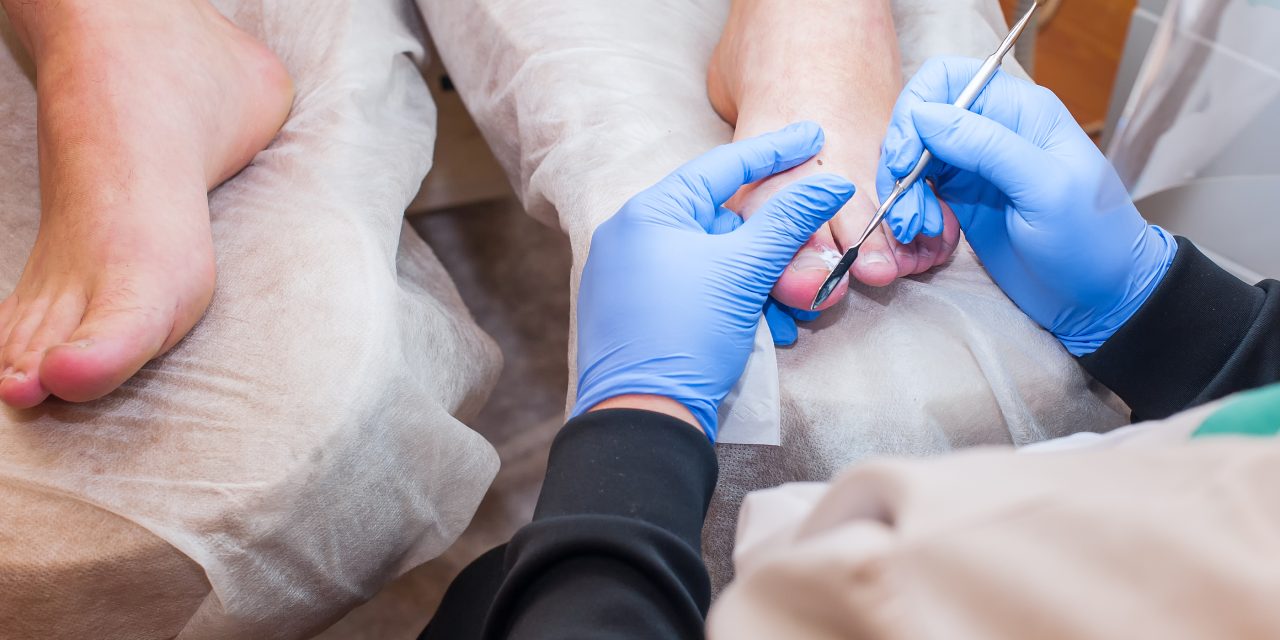
Medical Assessment and Diagnosis
Identifying fungal nail infections early is key to effective treatment. Consulting a healthcare provider, such as a dermatologist or podiatrist, can provide a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
When to See a Doctor
For those with discolored, thickened, or brittle toenails, seeing a doctor is advisable. Some signs of serious infection include pain, swelling, or spreading infection to the skin.
Individuals with diabetes or weakened immune systems should prioritize medical attention, as infections can cause severe complications.
It is important not to ignore persistent symptoms, as untreated fungal infections can lead to further nail damage.
Regular check-ups can help manage or prevent these infections, making early medical consultation essential.
Role of Dermatologist and Podiatrist
Dermatologists specialize in skin and nail conditions, while podiatrists focus on foot health. Both play crucial roles in diagnosing and treating fungal toenail infections.
They may use tools like nail clippings or scrapings to confirm the presence of fungi. Imaging might be used if there is a concern about infection spreading to the bone.
Treatment options may include topical or oral antifungal medications. In severe cases, nail removal might be considered.
Both dermatologists and podiatrists work with patients to develop an effective treatment plan, considering individual health needs and potential side effects.
Conventional Toenail Fungus Treatments
Conventional treatments for toenail fungus include topical solutions, oral medications, and more advanced options. These treatments can help clear up infections and prevent recurrence.
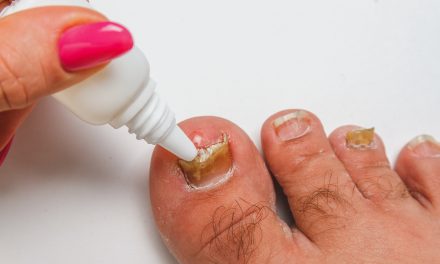
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are widely used for treating toenail fungus. Antifungal creams and solutions are applied directly to the nail and surrounding skin.
Common topical antifungals include ciclopirox, efinaconazole, and tavaborole. These medications work by inhibiting fungal growth.
While topical treatments can be effective, they often require prolonged use. For some, success is measured in months, not weeks.
Products like Jublia (efinaconazole) may take a year to show full results. Consistent application is key to achieving the best outcomes.
Oral Medications
Oral antifungals are another option for treating toenail fungus. Medications such as terbinafine (Lamisil) and itraconazole are commonly prescribed. They work by killing the fungus from the inside out.
Oral medications can have a higher success rate compared to topicals.
However, they often come with side effects. These can include liver damage, so physicians usually monitor liver function during treatment.
Despite these risks, many find oral antifungals effective in clearing up stubborn infections.
Advanced Options
For persistent toenail fungus, more advanced treatments might be needed.
Laser treatment is one option that targets fungi using concentrated light. This treatment seeks to eliminate the infection by penetrating the nail.
Though promising, laser treatments can be costly and are not always covered by insurance.
Surgery might also be considered in severe cases, where removal of the affected nail is necessary. Each option should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for the individual.
Home Remedies and Natural Options
Many people seek natural remedies to combat fungal infections in toenails. Essential oils and common household products can offer relief and aid in treatment.
Essential Oils and Extracts
Essential oils like tea tree oil and snakeroot extract are commonly used for nail fungus. Tea tree oil has natural antifungal properties. To use it, apply the oil directly on the affected nail once or twice a day.
Snakeroot extract, derived from a plant known for its antifungal abilities, can also help. Regular application may improve symptoms, though more research is needed to understand its full effects.
These oils should be used consistently. They can be combined with a carrier oil if skin irritation occurs.
It’s important that users monitor the nail for changes during treatment.
Alternative Household Products
Some household products can help with toenail fungus. Vinegar and apple cider vinegar are popular.
Soaking the affected foot in a mix of water and vinegar for about 15-20 minutes daily can reduce fungal growth.
Vicks VapoRub is another remedy sometimes used. Applying a small amount daily may show results.
Listerine, known for its antiseptic properties, might also provide benefits when used as a foot soak.
Garlic is another option. Crushing garlic cloves and applying them to the nail may help because of its antifungal properties.
These alternatives should be used with caution and those trying them should evaluate their effectiveness over time.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Toenail fungal infections, also known as onychomycosis, can be challenging to manage. Several factors increase the risk of infection, and understanding these can help in preventing the condition. The following sections outline common risk factors and practical ways to prevent toenail fungus.
Understanding Contributing Factors
Several risk factors make individuals more susceptible to toenail fungal infections.
People with diabetes or a weakened immune system are at increased risk because their bodies are less effective at fighting off infections. A weak immune system also makes recovery slower once an infection is established.
Athlete’s foot, a common fungal infection of the skin, can spread to the toenails if not treated promptly. Public areas, such as swimming pools and locker rooms, present a risk if proper hygiene is not maintained.
Improper footwear can exacerbate the problem. Tight shoes and socks that do not allow the feet to breathe create a warm, moist environment ideal for fungal growth.
Recognizing and modifying these risk factors is essential in reducing the likelihood of toenail infections.
Daily Habits for Prevention
Adopting specific daily habits can significantly aid in preventing toenail fungus.
Wearing protective footwear in public areas where moisture and fungi are prevalent is important.
Choose well-ventilated shoes and moisture-wicking socks to keep feet dry.
Practice proper foot hygiene by washing feet regularly and drying them thoroughly, especially between the toes. This practice helps prevent the buildup of moisture, a key factor in fungal growth.
Regularly trimming toenails to keep them short and clean reduces the surface area where fungus can grow.
Use antifungal powders or sprays on feet and in shoes as preventative measures.
These habits can create an environment that helps to prevent toenail fungal infections effectively.
Navigating Treatment for Special Populations
When dealing with fungal infections of the toenail, special populations such as diabetics and immunocompromised individuals require careful attention. These groups often face unique challenges and risks that influence treatment choices and outcomes.
Managing Fungal Infections in Diabetics
Individuals with diabetes need to be particularly cautious about fungal toenail infections.
The compromised blood flow in diabetics can lead to delayed healing and increased risk of complications. Thickened toenails may cause pressure, leading to ulcers or infections. Early intervention is crucial.
Topical antifungal treatments may be preferred for those who wish to avoid systemic effects of oral medications, but these often require prolonged use.
It’s important for diabetics to regularly monitor their feet for any changes and consult healthcare providers promptly to adjust treatment as necessary.
Routine foot care that includes keeping feet clean and dry can prevent further complications.
Treatment Considerations for the Immunocompromised
Those with a weakened immune system, such as organ transplant recipients or individuals undergoing chemotherapy, are at increased risk of complications from fungal toenail infections. Their bodies might not effectively combat infections, necessitating a more aggressive treatment approach.
Oral antifungal medications may be prescribed due to their efficacy, but they come with potential side effects and require monitoring of liver function.
Topical treatments are also an option but might be less effective.
Maintaining foot hygiene and avoiding trauma to toenails can help in managing risks. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for timely intervention and to tailor treatment plans to individual needs.
Aftercare and Monitoring
Proper aftercare is crucial in preventing the recurrence of fungal infections in toenails. It involves careful nail care and being alert to any signs of recurrence, ensuring healthy nails and reducing the risk of future infections.
Post-Treatment Nail Care
Post-treatment nail care is essential to maintain nail health and prevent future infections.
Regular trimming with clean nail clippers can help keep nails short and manageable. It’s important to disinfect the clippers before and after use to avoid transferring any fungus.
Using moisturizing cream can help keep nails and surrounding skin hydrated, which may help in maintaining nail health.
Wearing breathable footwear and moisture-wicking socks can prevent the damp conditions that fungi thrive in. Foot hygiene is key; keeping feet clean and dry can make a significant difference.
Changing socks daily and using powder to keep feet dry can also help.
Using antifungal sprays or powders on feet and shoes as a preventive measure might reduce risk factors.
Keeping toenails in good shape might lower the chance of infection coming back.
Recognizing Signs of Recurrence
Understanding the signs of recurrence is important for timely intervention.
Discolored nails are often a red flag indicating that the infection might be returning. Such nails may appear yellow or brown.
Thickening of the nails can also point to a recurrence of fungal infections.
Other signs to watch for include crumbling or brittleness in the nails.
Should these symptoms appear, consulting a healthcare professional promptly is advised.
Maintaining good nail health involves regular checks for these signs to catch any problems early.
Keeping an eye out for these signs can prevent more serious infections. This vigilance in monitoring may make a big difference in overall foot and nail health.
Advanced and Surgical Interventions
Treatment for toenail fungal infections can include advanced options, such as laser treatments and surgical interventions, especially when traditional methods fail. These approaches, though more involved, can be effective in severe cases or when a rapid response is needed.
When Surgery Is Recommended
Surgery for toenail fungus involves removing the infected nail. This approach is considered when the infection is severe or causes significant pain.
Complete nail removal may be permanent, allowing antifungal treatments to target any remaining infection sites. Partial nail removal, less drastic, allows for quicker nail regrowth. This option is often combined with medication for effective results.
Surgery is also useful when other treatments, such as topical or oral medications, have proven ineffective. A healthcare provider usually recommends surgery after thorough examination and evaluation.
The Role of Laser Treatments in Toenail Fungus
Laser treatments are gaining popularity for their precision and effectiveness. Dermatophyte fungi, which often cause nail infections, can be targeted by the heat generated from lasers.
This treatment aims to kill the fungus without damaging surrounding tissue. Patients often choose laser treatments due to minimal recovery time and lack of side effects compared to oral medications.
However, successful outcomes may require multiple sessions. It’s important to consult healthcare professionals to evaluate if laser treatment is suitable, considering factors like the infection’s severity and patient health. For more information on laser treatments and their prospects, refer to this article.
Frequently Asked Questions
Toenail fungus can be stubborn, but there are effective ways to manage it. This section answers common questions about treatments, signs of recovery, and possible complications.
What is the most effective treatment for toenail fungus?
Prescription antifungal medications are often the most effective. Oral treatments, such as terbinafine, are commonly prescribed, while topical solutions may also be used.
In certain cases, treatments like intermittent itraconazole may be considered.
How can you tell if toenail fungus is healing?
Signs of healing include new, clear nail growth where discoloration used to be and the reduction of nail debris. It is vital to be patient, as full recovery can take several months due to the slow nature of nail growth.
What are the best home remedies to kill toenail fungus?
Some people try home remedies such as tea tree oil, vinegar soaks, or Vicks VapoRub. While these may provide relief for mild cases, their effectiveness may vary.
Consistent use is key, but results should be monitored, and severe cases should seek medical advice.
Which over-the-counter treatments work best for toenail fungus?
Over-the-counter antifungal creams and ointments can help in mild cases. Ingredients like clotrimazole or undecylenic acid are often found in these products.
They may be less effective than prescription options but can be useful when used consistently.
Is it possible for toenail fungus to lead to more serious health problems?
In rare cases, untreated toenail fungus could lead to complications, especially in people with weakened immune systems or diabetes. It can cause painful nails or secondary infections, so timely intervention is crucial.
How can toenail fungus be removed safely at home?
Basic hygiene measures can help manage toenail fungus. Regularly trimming and cleaning nails, and maintaining dry feet can prevent further infection. Using antifungal sprays or powders is also recommended. For significant cases, consult a healthcare provider for more guidance.