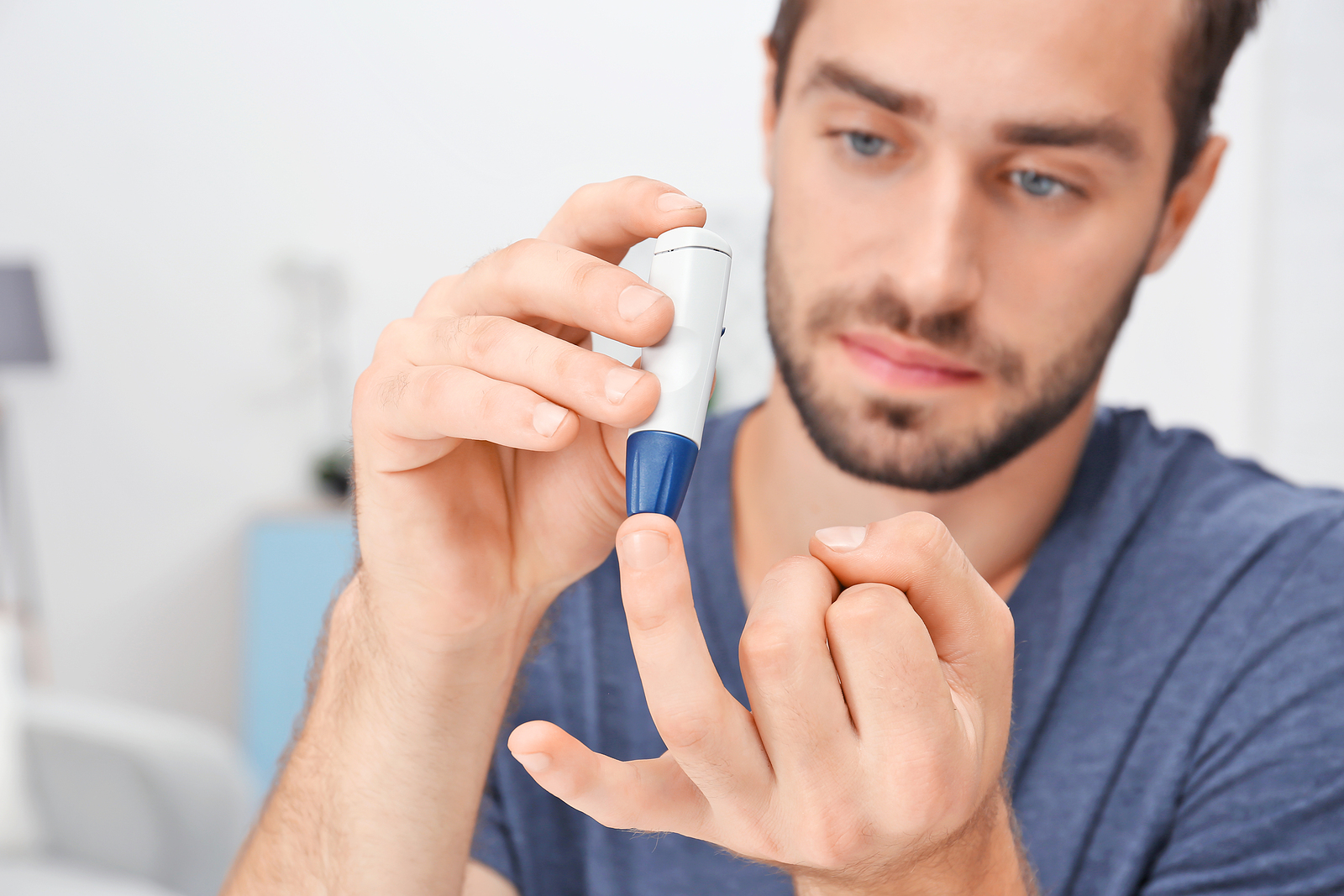
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use it effectively, resulting in high blood sugar levels. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1, where the body does not produce any insulin, and type 2, where the body does not use insulin properly. Although there is currently no complete cure for diabetes, there are ways to manage and, in some cases, reverse the condition, particularly for type 2 diabetes.

Managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. By understanding the different aspects of diabetes, individuals can take control of their health and minimize complications. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans.
Key Takeaways
- Managing diabetes combines lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and blood sugar monitoring.
- Type 2 diabetes, in some cases, can be reversed through diet and weight loss.
- Effective diabetes management helps prevent complications and improve overall health.
Understanding Diabetes
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels. There are several types of diabetes, including type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and prediabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes, the most common form, occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin, and the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Gestational diabetes develops in pregnant women and usually resolves after giving birth, but it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Prediabetes, a condition marked by elevated blood sugar levels, may progress into type 2 diabetes if not managed through lifestyle changes and medication.
Role of the Pancreas
The pancreas plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels by producing the hormone insulin. Insulin is produced in the pancreas by specialized cells called beta cells. Insulin helps cells in the body absorb glucose from the bloodstream, providing them with energy. In diabetics, either the beta cells are destroyed (type 1 diabetes) or the body becomes resistant to insulin (type 2 diabetes), leading to high blood sugar levels.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for the cells in the body, including brain cells. Maintaining proper blood sugar levels is essential for overall health. The body regulates glucose levels through a delicate balance between insulin and glucagon, another hormone produced by the pancreas. When blood sugar levels are too high, the pancreas releases insulin to help the cells take in glucose. Conversely, when blood sugar levels are too low, the pancreas releases glucagon to stimulate the liver to release stored glucose.
In diabetics, this balance is disrupted. In type 1 diabetes, the lack of insulin production leads to elevated blood sugar levels, while in type 2 diabetes, the cells become resistant to insulin, and the pancreas can’t keep up with the demand for insulin to regulate glucose levels. Managing diabetes involves maintaining blood sugar levels within a target range through a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and, in some cases, insulin therapy.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Blood Tests
There are several blood tests used to diagnose and monitor diabetes. These tests provide insight into an individual’s blood sugar levels, which is essential for managing the condition.
- Random Blood Sugar Test: This test measures blood sugar levels at a random point in time, regardless of when you last consumed food or drink. A level of 200 mg/dL or higher can indicate diabetes .
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: This test measures blood sugar levels after fasting for at least 8 hours. Normal fasting glucose is below 100 mg/dL, while prediabetes is diagnosed at 100-125 mg/dL, and diabetes at 126 mg/dL or higher .
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: This test checks blood sugar levels before and two hours after consuming a sugary drink. A level less than 140 mg/dL is normal, 140-199 mg/dL indicates prediabetes, and 200 mg/dL or higher signifies diabetes .
- A1C Test: The A1C test measures your average blood sugar level over the past 2 to 3 months. It provides a more comprehensive view of glucose control compared to the previously mentioned tests. An A1C level below 5.7% is considered normal, 5.7-6.4% indicates prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher on two separate tests confirms a diagnosis of diabetes .
Table 1: Blood Test Reference Ranges
| Test | Normal | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Blood Sugar Test | < 200 mg/dL | N/A | ≥ 200 mg/dL |
| Fasting Blood Sugar Test | < 100 mg/dL | 100-125 mg/dL | ≥ 126 mg/dL |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test | < 140 mg/dL | 140-199 mg/dL | ≥ 200 mg/dL |
| A1C Test | < 5.7% | 5.7-6.4% | ≥ 6.5% |
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is a more advanced method for tracking blood sugar levels. Users wear a small sensor under their skin that measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid between cells over time. The sensor sends readings to a glucose meter, smartphone, or other devices, providing real-time data and trend analysis.
CGM helps people with diabetes make more informed decisions about insulin dosing, food intake, and physical activity. It can also alert users to dangerously high or low glucose levels, preventing severe hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. However, users should still confirm their blood sugar levels using a glucose meter before making treatment adjustments, as CGM readings can occasionally be inaccurate 5.
In conclusion, accurate diagnosis and monitoring of diabetes are crucial for effective management of the condition. Blood tests and continuous glucose monitoring provide essential information to help individuals and healthcare professionals make informed decisions about treatment.
Lifestyle Management
Dietary Adjustments
Making dietary adjustments is a critical component of managing diabetes. A balanced diet promoting healthy eating habits can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Emphasizing carbohydrates, which greatly affect blood glucose levels, is vital. Choosing high-quality carbs like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables rich in fiber is essential.
Balancing carbohydrate intake with protein, which can help maintain stable blood sugar levels, is also crucial. High-quality protein sources include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based alternatives like tofu and legumes. Monitoring portion sizes can also contribute to weight loss and better blood sugar control. A helpful suggestion is to follow the “plate method,” where 1/2 of each plate consists of non-starchy vegetables, 1/4 is lean protein, and 1/4 is high-quality carbohydrates.
Physical Activity and Exercise
Engaging in physical activity and exercise is essential to manage diabetes. Both aerobic exercise and strength training can significantly benefit people with diabetes. Aerobic exercise includes walking, swimming, or cycling, aiming for at least 150 minutes weekly. This type of exercise helps improve cardiovascular health and assists in weight loss.
Besides, it’s essential to incorporate regular strength training into the exercise routine. By building muscle mass, one’s body becomes more efficient at using insulin and processing glucose. Aim for two or more days of strength training each week, targeting all major muscle groups.
Combining lifestyle changes like dietary adjustments and regular exercise can make a significant difference in diabetes management. By maintaining healthy habits and being mindful of blood sugar levels, people with diabetes can improve their overall health and reduce their risk of complications.
Medical Treatments
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is a crucial aspect of diabetes treatment for people with type 1 diabetes and, in some cases, type 2 diabetes. Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels and prevent diabetes complications. There are different types of insulin available depending on the individual’s needs. These include rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin.
Insulin can be administered in various ways, such as:
- Subcutaneous injections using a syringe or insulin pen
- Insulin pump, which delivers a continuous flow of insulin
- Inhaled insulin, which is a newer method of administering insulin
Oral Medications
Oral medications are commonly used for managing type 2 diabetes, as they help control blood sugar levels by targeting different aspects of glucose regulation. Some of the common oral medications include:
- Metformin: This medication is often the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes. Metformin reduces glucose production in the liver and increases insulin sensitivity in cells.
- Sulfonylureas: These medications stimulate the pancreas to produce and release more insulin. Examples include glipizide, glyburide, and glimepiride.
- Thiazolidinediones: These drugs help improve insulin sensitivity by targeting the cells’ response to insulin. Examples include pioglitazone and rosiglitazone.
- SGLT2 inhibitors: This class of medications reduces glucose reabsorption in the kidneys and increases glucose excretion in the urine, resulting in lower blood sugar levels. Examples include canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin.
It is essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable diabetes or combination of medications. This depends on the individual’s diagnosis, health, and other factors. Follow the prescribed treatment plan and monitor blood sugar levels regularly to ensure optimal diabetes management.
Advanced Treatment Options

Apart from traditional methods to manage diabetes, some advanced treatment options can help patients with severe cases of the disease. In this section, we discuss two such options: bariatric surgery and pancreatic transplantation.
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, has been shown to be an effective treatment for some patients, particularly those with type 2 diabetes who are significantly overweight. Through surgical procedures such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, the size of the stomach is reduced, resulting in a decrease in the amount of food consumed and eventually, weight loss.
There are several benefits of bariatric surgery for diabetes patients, including improvements in blood sugar control and a reduction in the need for diabetes medications. However, it’s important to note that bariatric surgery is not a cure for diabetes, and patients should maintain a healthy lifestyle and continue working closely with their healthcare team.
Pancreas Transplantation
Another advanced treatment option for patients with severe diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes, is a pancreas transplant. In this procedure, a healthy pancreas is transplanted from a deceased donor to a diabetes patient, allowing the patient’s body to produce insulin naturally once again.
While pancreas transplantation can dramatically improve the quality of life for some diabetes patients, it’s not without risks. Complications can include infection, rejection of the transplanted pancreas, and side effects from immunosuppressive medications needed to prevent organ rejection.
To determine if advanced treatment options like bariatric surgery or pancreas transplantation are appropriate, patients should consult a qualified healthcare professional who can evaluate their unique medical history and discuss these treatments’ potential risks and benefits.
Preventing Complications

Managing Cardiovascular Risk
People with diabetes must manage their cardiovascular risk to reduce the likelihood of heart disease. One important measure is controlling blood pressure, as high blood pressure can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. Monitoring blood pressure regularly and making appropriate lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and reducing salt intake is recommended.
Another key factor is managing cholesterol levels. High cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. A balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats, along with regular physical activity, can help control cholesterol levels. Medications may also be prescribed if needed. In particular, statins are often recommended for individuals with diabetes to manage cholesterol and reduce cardiovascular risk.
Protecting Kidney Health
Diabetes can lead to chronic kidney disease, eventually causing kidney failure if not managed well. Protecting kidney health is vital for individuals with diabetes. Regular monitoring of kidney function through blood and urine tests is crucial for early detection of any issues.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is critical in preventing diabetic kidney damage. It’s essential to follow a diabetes management plan, including medication, a well-balanced diet, and consistent physical activity. Additionally, blood pressure control is vital, as hypertension can further damage the kidneys.
Lastly, it’s essential to protect one’s liver. Although diabetes is more commonly associated with the kidneys and heart, liver health should also be considered. A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can contribute to preventing liver complications related to diabetes.
In conclusion, managing cardiovascular risk and protecting kidney health are essential for people with diabetes to avoid complications. By keeping blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels in check, individuals with diabetes can maintain their overall health and prevent further damage to vital organs.
Remission and Management

Achieving Remission
Type 2 diabetes remission is a state where blood sugar levels return to normal levels without the need for diabetes medication. Although it is not considered a cure, achieving remission can significantly improve overall health and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and healthy weight can contribute to this goal.
An important factor in achieving remission is healthy weight management. This can be accomplished through:
- Balanced diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Portion control: Reducing portion sizes to manage calorie intake.
- Physical activity: Engaging in regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or biking, for at least 150 minutes per week.
Monitoring blood sugar levels is also crucial in the path towards remission. This helps individuals track their progress and adjust their diet, exercise, or medication.
Chronic Disease Management
Although type 2 diabetes is often considered a lifelong condition, proper management of the disease can minimize its impact on daily life and long-term health. Some key aspects of chronic disease management include:
- Blood sugar monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar levels helps individuals maintain glycemic control and adjust their treatment plan if necessary.
- Medication adherence: Taking prescribed medications as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Regular exercise: Staying active improves insulin sensitivity, helps control blood sugar levels, and supports weight management.
- Healthy eating habits: Consuming a balanced diet, rich in nutrients and low in added sugars, can effectively manage blood sugar levels.
- Routine medical checkups: Regular visits to healthcare providers allow for close monitoring and prevention of diabetes-related complications.
In summary, attaining type 2 diabetes remission and managing the disease effectively require lifestyle changes, blood sugar monitoring, and regular communication with healthcare providers. While remission may not be possible for everyone, the proper management approach can significantly improve the quality of life for those living with this chronic disease.
Support and Resources

Working with Healthcare Professionals
When managing diabetes, working closely with healthcare professionals specializing in the condition is essential. One such specialist is an endocrinologist who focuses on hormone-related disorders, including diabetes. They can help develop a personalized treatment plan considering an individual’s medical history and lifestyle.
In addition to endocrinologists, a registered dietitian can offer valuable support and guidance. They can help create a tailored meal plan considering the individual’s food preferences and nutritional needs. By working with healthcare professionals, an individual can achieve better blood sugar control and minimize complications.
Diabetes Associations and Support Groups
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) is a leading organization for diabetes research, education, and advocacy. They provide a wealth of resources, such as educational programs, toolkits, and support groups, to help individuals manage their condition. By participating in the ADA’s events, like the Tour de Cure® and Step Out Walk to Stop Diabetes®, individuals can join a community of people affected by diabetes, raising funds and awareness to combat the disease.
Various support groups are available for individuals with diabetes, as well as their family and friends. These groups offer emotional support, practical advice, and valuable insights from others who understand the challenges of living with diabetes. Joining a support group can help individuals feel less isolated and empower them to take control of their health journey.
Staying proactive, informed, and connected is essential when living with diabetes. By working with healthcare professionals and engaging with support networks, an individual can build a solid foundation for managing their condition and maintaining overall well-being.
Innovations in Diabetes Care

Research Advances
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic and complex autoimmune disease affecting a significant portion of the global population. Recent research advances have contributed to greater understanding and potential treatments for the condition. One notable area of research is the use of stem cells in the treatment of diabetes. Scientists are exploring the potential of these undifferentiated cells to regenerate damaged pancreas cells, potentially restoring insulin production in individuals with diabetes.
Another exciting research development is focused on understanding the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and diabetes risk. Studies suggest that maintaining a healthy BMI can help prevent the onset of diabetes and other related complications. Additionally, these findings highlight the importance of promoting healthy lifestyle changes to control and prevent the condition.
Technological Developments
Beyond research, numerous exciting technological developments have emerged to help individuals manage their diabetes. Some of these innovations include:
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): These devices provide real-time data on blood sugar levels, helping patients make informed decisions about their diet and medication.
- Insulin Pumps: These devices deliver insulin continuously throughout the day, mimicking the natural insulin secretion of a healthy pancreas.
- Artificial Pancreas Systems: Also known as closed-loop systems, these devices combine CGMs and insulin pumps to adjust insulin delivery automatically based on real-time blood sugar data.
In summary, significant research and technological advancements in diabetes care have led to innovative treatments and management strategies, improving the quality of life for individuals affected by this chronic condition. Combining stem cell research, understanding the importance of BMI, and developing new technologies all contribute to a promising future for diabetes care.
Conclusion

Adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity are essential in managing diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes. Though not a guaranteed cure, lifestyle changes have been proven effective in reversing or controlling the condition in some cases.
A nutritious and well-balanced diet forms the cornerstone of diabetes management. Maintaining a healthy diet can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications. It is crucial to individualize dietary plans based on factors such as age, weight, gender, health condition, and occupation.
Physical activity plays a significant role in diabetes management. Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of heart disease. Combining a healthy diet and exercise can result in effective weight management.
While there is no universally accepted cure for type 2 diabetes, some evidence suggests that the disease can be reversed in certain instances through lifestyle modifications, weight loss, and bariatric surgery. However, it is essential to note that the remission of type 2 diabetes varies among individuals.
In conclusion, making lifestyle changes and maintaining a healthy diet, coupled with regular physical activity, can contribute to better management and control of diabetes. While a complete cure for type 2 diabetes remains elusive, these measures can effectively improve the quality of life for those living with the condition.
Frequently Asked Questions

What are effective lifestyle interventions to reverse type 2 diabetes?
Several lifestyle interventions can effectively reverse type 2 diabetes. These include maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and losing excess weight. A balanced diet with low-carb, high-fiber foods and lean proteins can help manage blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or biking, can lower blood glucose and improve insulin sensitivity.
Can a significant weight loss lead to the remission of type 2 diabetes?
Yes, significant weight loss can potentially lead to remission of type 2 diabetes. In some cases, individuals who lose 5% to 10% of their body weight can experience substantial improvements in blood sugar control, insulin sensitivity, and overall health. However, it’s important to note that weight loss should be accomplished through healthy means, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, and maintained over time for sustained results.
What measures can be taken to manage and potentially reverse early-stage diabetes?
At the early stages of diabetes, it is critical to implement lifestyle changes such as proper nutrition, increased physical activity, and weight management. Regular blood sugar monitoring and adherence to prescribed medications can also help manage and potentially reverse early-stage diabetes. Consulting with a healthcare professional to tailor a personalized treatment plan is important.
Are there any breakthrough treatments for type 1 diabetes on the horizon?
While there is no cure for type 1 diabetes, research is continually evolving with breakthroughs in treatments and management methods. Some promising advancements include stem cell therapies, artificial pancreas systems, and immunotherapies. However, it is essential to remember that these breakthroughs are still in development and may not be available for widespread use.
How can one manage diabetes to increase life expectancy and quality of life?
Effective diabetes management involves monitoring blood sugar, maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in physical activity, and taking prescribed medications as directed by a healthcare provider. Proper management can result in better blood sugar control, minimized complications, and increased life expectancy. Additionally, comprehensive diabetes education and support can improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition.
What are the natural methods to prevent the onset of diabetes?
Natural prevention methods for diabetes include maintaining a healthy body weight, consuming a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, and participating in regular physical activity. Reducing the intake of processed and high-sugar foods, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep are also essential factors in preventing the onset of diabetes.