Type 2 diabetes is a growing health concern worldwide, affecting millions. It is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for over 90% of all cases globally.
In 2015, it was estimated that 415 million people had some form of diabetes, and most of them had type 2 diabetes. By 2040, this number could jump to 642 million people. This shows the urgent need for awareness and action.

In the United States alone, millions of people live with type 2 diabetes. As the numbers increase, it’s crucial to understand this condition, its risk factors, and ways to prevent or manage it effectively.
Type 2 diabetes often develops in adults, though it’s becoming more common in younger populations too. Being informed about the symptoms, lifestyle choices, and treatment options can make a big difference.
Awareness about type 2 diabetes is important not only for individuals but also for communities and countries. The economic impact is significant, with high healthcare costs and loss of productivity. Efforts to educate and inform the public can help reduce the long-term effects.
Key strategies include a healthy diet and regular exercise, which are essential components in preventing and managing type 2 diabetes. Research and advances in treatment continue to offer hope for those affected by this condition.
Key Takeaways
- Millions of people worldwide have type 2 diabetes.
- Prevention and management are crucial for reducing impact.
- Awareness and lifestyle changes can make a difference.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes

Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar. It largely involves insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin.
Defining Diabetes and Its Types
Diabetes mellitus is a group of disorders characterized by high levels of blood sugar. The most common forms are Type 1 and Type 2.
In Type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin at all. Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for more than 90% of cases, is caused by insulin resistance. This resistance causes the pancreas to produce more insulin, but over time, it cannot keep up. This results in elevated blood glucose levels.
Factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and diet play roles in its development.
The Role of Insulin and Blood Sugar
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps cells absorb glucose from the blood.
In Type 2 diabetes, cells become resistant to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar. Over time, high blood glucose can result in complications like heart disease and nerve damage.
Managing blood sugar is crucial to prevent such complications. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and medications like metformin help regulate insulin and blood glucose levels.
Innovative research aims to further explore the relationship between insulin and blood sugar to develop new treatments.
Global and National Prevalence

Type 2 diabetes is a growing concern worldwide, touching nearly every corner of the globe. Both global statistics and national data provide insight into how widespread this condition has become.
Diabetes Statistics Worldwide
Globally, type 2 diabetes affects millions of people. Estimates suggest that there are at least 300 million individuals dealing with obesity and diabetes. The International Diabetes Federation predicts even more cases by 2045.
Furthermore, variations in diabetes prevalence are seen across different regions. Countries lacking national databases face challenges in understanding the full impact of diabetes, which complicates efforts in prevention and treatment.
Type 2 Diabetes in the United States
In the United States, type 2 diabetes has reached alarming levels. According to the National Diabetes Statistics Report, millions are affected. Increased obesity rates contribute significantly to this prevalence.
Healthcare systems are under pressure due to the growing number of patients requiring treatment. The national burden of diabetes continues to rise, intensifying the need for effective policies and interventions to manage and prevent the disease.
Risk Factors and Prevention

Type 2 diabetes is a common condition influenced by various risk factors and lifestyle choices. Understanding these elements is vital to managing and preventing the disease.
Identifying Common Risk Factors
Many risk factors are linked to the development of type 2 diabetes. Obesity stands out as a significant contributor. People with a higher body mass index (BMI) are at increased risk.
Family history also plays a role. Those with relatives who have diabetes are more likely to develop the condition.
Prediabetes is another important indicator, where blood sugar levels are higher than usual but not yet high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. Recognizing and addressing these risk factors early can be crucial in delaying or preventing the disease.
The Impact of Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices greatly affect the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. A healthy diet and regular physical activity are key.
Diets high in sugar and low in nutrients contribute to weight gain and increased diabetes risk.
Being active helps maintain a healthy weight and improves insulin sensitivity, which is important for blood sugar regulation. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also increase diabetes risk.
By making conscious lifestyle choices, individuals can reduce their chances of developing the disease and improve overall health.
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
Preventive measures focus heavily on lifestyle changes. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can significantly reduce the risk.
Individuals with prediabetes benefit from regular screening to monitor blood sugar levels.
Programs emphasizing weight loss and increased physical activity have proven effective. It is important to set realistic goals and seek support if needed.
Simple changes, like substituting sugary drinks for water and taking regular walks, make a difference. Early intervention is beneficial in preventing progression to diabetes.
Economic Impact of Type 2 Diabetes

Type 2 diabetes poses a significant economic burden, affecting both society and individuals. The costs associated with managing and treating this condition are substantial, with implications for public health budgets and personal finances.
The Cost of Diabetes to Society
The societal costs of type 2 diabetes are extensive. This includes direct costs such as hospital visits, medication, and medical supplies. Additionally, there are indirect costs like lost productivity and reduced workforce participation due to health complications.
The treatment and management of diabetes contribute significantly to healthcare spending globally.
In developed nations, an increase in type 2 diabetes prevalence is expected, affecting national economies. The economic burden is heavy, especially in healthcare systems already dealing with other chronic illnesses.
Policies that focus on prevention and efficient management could help reduce expenses. For more information on global studies of economic costs, you can view the review of these expenses.
Individual Financial Burden
On a personal level, people with type 2 diabetes face significant financial challenges. The costs for medication, frequent doctor visits, and potential emergencies add up over time.
Uninsured individuals or those with limited coverage may find it particularly hard to manage expenses.
Out-of-pocket costs vary based on insurance, medication, and individual health needs.
The personal financial impact can lead to a reduction in quality of life as individuals may prioritize spending on diabetes management over other needs. Additionally, the potential for reduced earnings due to absenteeism or decreased productivity at work further compounds the situation. More detailed information on the economic impact is available for exploration.
Complications and Comorbidities
Type 2 diabetes can lead to various health issues. People with this condition may face short-term problems like high blood sugar levels, as well as long-term health challenges that affect different body organs.
Short-Term Complications
People with type 2 diabetes may experience complications that need immediate attention. One common issue is hyperglycemia, where the blood sugar levels become too high. This can lead to thirst, frequent urination, and even fatigue.
If left untreated, it might evolve into a more serious condition known as diabetic ketoacidosis. Here, the body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones, which require emergency medical treatment.
Another short-term complication can arise when blood sugar levels drop too low, known as hypoglycemia. Symptoms include dizziness, shaking, and confusion.
Proper management, including monitoring blood sugar levels and adhering to a treatment plan, is essential to prevent these complications.
Long-Term Health Challenges
Over a longer period, uncontrolled type 2 diabetes can result in severe health issues, affecting organ function and increasing mortality risks.
Cardiovascular diseases are common among diabetes patients, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes. Kidney disease or diabetic nephropathy is also prevalent, causing reduced kidney function.
Vision problems such as diabetic retinopathy occur due to damage to the blood vessels in the retina, potentially leading to blindness. Nerve damage, or neuropathy, is another concern, which can cause pain and numbness, particularly in the legs and feet.
These long-term health challenges underline the importance of regularly monitoring and managing diabetes.
Diabetes Management and Treatment
Managing type 2 diabetes involves a combination of monitoring, medical interventions, and lifestyle changes. These elements work together to help control blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
Monitoring and Controlling Blood Glucose
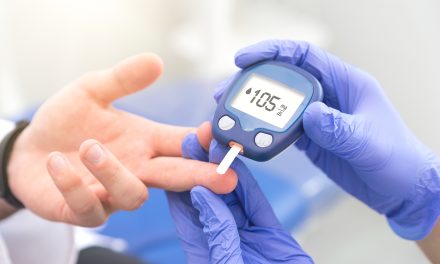
Consistently checking blood glucose levels is crucial for people with type 2 diabetes. This can be done using a glucometer, which provides immediate results.
People should aim to maintain their blood glucose levels within the target range set by their healthcare team.
Daily checks can guide dietary choices and physical activity levels. Keeping a log of these readings helps in understanding patterns and effects of different foods and activities.
Continuous glucose monitors are also an option for real-time data. These devices track glucose levels throughout the day without frequent finger pricks.
Medical Interventions and Insulin Therapy
Medication plays a significant role in managing type 2 diabetes. Several drugs help lower blood glucose, including Metformin, which decreases liver glucose production. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors are another option, impacting glucose excretion in the kidneys.
Insulin therapy might be necessary when other medications are insufficient. Insulin can be injected using pens or pumps to regulate glucose levels.
Healthcare providers determine the best type of insulin and dosage based on individual needs. Regular medical check-ups ensure treatment plans remain effective and adjusted as needed.
Education and Lifestyle Modification
Education is key in managing diabetes. A diabetes educator can provide valuable guidance on managing the disease. They offer personalized advice on making lifestyle changes such as healthier eating and increasing physical activity.
Lifestyle modifications include regular exercise, which helps lower blood glucose levels and maintain a healthy weight. Activities like walking, cycling, or swimming are excellent choices.
Eating a balanced diet with controlled carbohydrates, lean proteins, and vegetables provides nutritional benefits without spiking blood sugar. Through these strategies, individuals can better manage their diabetes and improve their quality of life.
Special Populations and Diabetes
The impact of type 2 diabetes varies greatly among different groups. Certain ethnicities, life stages like pregnancy, and age groups such as youth face unique challenges. Addressing these variations is key to managing and understanding type 2 diabetes effectively.
Diabetes in Different Ethnic Groups
Diabetes affects various ethnic groups in distinct ways. Among American Indians and Alaska Natives, the rates of type 2 diabetes are significantly high, partly due to genetic and lifestyle factors. Non-Hispanic Blacks and Hispanics also experience a higher prevalence compared to Non-Hispanic Whites.
Cultural factors, access to healthcare, and socioeconomic status contribute to these disparities. Non-Hispanic Asians can face unique risk factors often linked to diet and body composition. Recognizing these challenges helps create targeted interventions that can enhance prevention and management in these groups.
Type 2 Diabetes and Pregnancy
Pregnancy increases the complexity of managing type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes is a concern as high blood sugar levels during pregnancy can affect both the mother and child. It raises the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life for both.
Close monitoring and adjusting medications are essential during this period to maintain safe blood sugar levels. Doctors often recommend lifestyle changes like a balanced diet and regular exercise to manage the condition effectively. Women with preexisting diabetes require special care to ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome.
Diabetes Among Youth and Adolescents
Type 2 diabetes is rising among youth, particularly in those with ethnic backgrounds that show higher adult prevalence. This increase is linked to rising obesity rates, sedentary lifestyles, and poor diet habits.
Diagnosis at a young age is alarming because it implies longer-term health issues.
Youth face unique challenges like managing diabetes during growth and dealing with peer pressure. Early intervention, educational programs, and family support play critical roles in managing diabetes in this age group.
Addressing these factors helps mitigate health risks and improve quality of life for young people with diabetes.
Research and Future Outlook
The research on type 2 diabetes is continuously evolving, providing new insights and fostering the development of innovative solutions.
Major public health initiatives aim to reduce the burden of diabetes through awareness and education.
Advancements in Diabetes Research
Research into type 2 diabetes has led to a better understanding of genetic factors and new treatment options. Studies have identified common genetic variants linked to glycemic control, improving personalized treatment plans.
Additionally, the development of diabetes technology, like continuous glucose monitors, has transformed management strategies.
Organizations like the American Diabetes Association and ongoing studies use real-time data and advanced analytics to improve prevention and management. The potential for new medications and lifestyle intervention strategies continues to grow, offering hope for those affected by diabetes around the globe.
Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives play a critical role in combating type 2 diabetes. The U.S. Diabetes Surveillance System actively monitors diabetes trends, providing valuable data to shape health policies.
Efforts also focus on promoting healthier lifestyles and increased access to medical care, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where resources are limited.
Programs that encourage regular physical activity, healthy eating, and routine medical check-ups have been established in many communities.
Collaborations between government agencies and health organizations aim to reduce obesity and improve overall health, directly targeting factors contributing to diabetes.
Creating Awareness and Education
Raising awareness and educating the public about type 2 diabetes is crucial in managing the disease. Initiatives spearheaded by the American Diabetes Association and other groups focus on spreading knowledge about risk factors and prevention strategies.
Community outreach programs and educational campaigns are tailored to teach people about maintaining healthy lifestyles and recognizing early symptoms.
Social media and online platforms are leveraged to reach wider audiences, making information accessible to more people.
Targeted campaigns in both high-income and developing regions focus on reducing the global burden of disease by empowering individuals to take charge of their health through informed decisions and practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Type 2 diabetes is a widespread condition affecting millions around the world. Understanding statistics, demographics, and prognosis is key to better management and awareness.
What are the latest statistics on the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes globally?
Type 2 diabetes affects over 400 million people globally. Countries with large populations such as China and India see higher numbers, but the prevalence is rising in developed nations as well.
This trend is linked to lifestyle factors and increased urbanization.
What percentage of the diabetic population is affected by Type 2 as opposed to Type 1?
Approximately 90-95% of individuals with diabetes have Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is much less common and typically develops earlier in life.
The vast majority of adults with diabetes are managing Type 2 rather than Type 1.
How has the number of Type 2 diabetes cases changed over the past decade?
The past decade has seen a significant rise in Type 2 diabetes cases. Lifestyle changes, aging populations, and obesity are major contributors to this increase.
Many regions report yearly growth in new cases, prompting public health initiatives aimed at prevention and education.
At what age is someone most at risk for developing Type 2 diabetes?
People are most at risk of developing Type 2 diabetes after age 45. However, it’s becoming more common in younger individuals.
Factors such as sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, and family history can increase risk at earlier ages.
Can individuals with Type 2 diabetes expect to live a normal lifespan?
With proper management, individuals with Type 2 diabetes can expect to live a normal lifespan. This includes regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, healthy eating, physical activity, and medication adherence.
Early diagnosis and proactive care lead to better outcomes and quality of life.
How does the prognosis of Type 2 diabetes differ from Type 1 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes generally has a more favorable prognosis compared to Type 1 due to its later onset and different treatment requirements.
Many people with Type 2 can manage their condition with lifestyle changes and oral medications, while Type 1 requires life-long insulin management.
The management strategies and challenges differ between the two types.