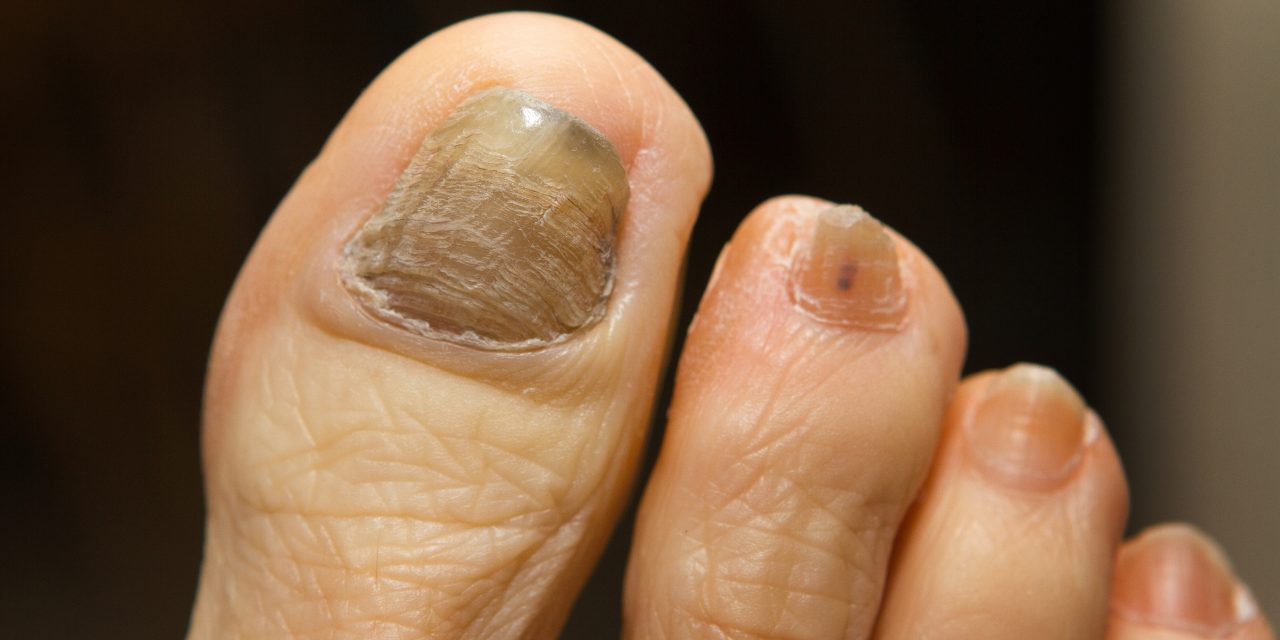
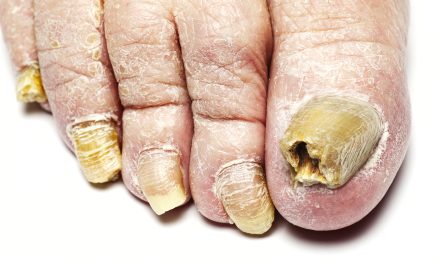
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While many may associate it with just cosmetic concerns, it is crucial to understand that, in some cases, it can indeed cause pain and discomfort. As with any health issue, early detection and proactive treatment are key to minimizing the potential negative effects on an individual’s daily life and overall well-being.
Understanding toenail fungus is instrumental in identifying whether the condition is causing pain. It is caused by a fungal infection in the nail bed, and if left untreated, it can lead to thickened, discolored, and brittle nails. Pain may develop as the fungal infection progresses, resulting in inflammation and pressure on the surrounding tissues. In more severe cases, the infected nail can separate from the nail bed, leading to increased pain and potential complications.
Key Takeaways
- Toenail fungus is more than a cosmetic concern and can cause pain and discomfort.
- Early detection and treatment are essential for minimizing the condition’s impact on daily life.
- Understanding the symptoms and signs of toenail fungus can help individuals take timely action.
Understanding Toenail Fungus
Causes of Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition caused by fungal pathogens. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, like those found in shoes and around public pools or showers. The most common causes of toenail fungus include:
- Dermatophytes: These fungi, such as Trichophyton rubrum, are the primary cause of toenail fungus and are responsible for about 90% of cases.
- Yeasts: Candida species can also cause toenail infections, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Molds: Non-dermatophyte molds can act as opportunistic pathogens leading to toenail fungus.
Factors that increase your risk of developing toenail fungus include:
- Age
- Wearing damp footwear or socks
- Frequent contact with contaminated surfaces
- Weakened immune system
- Minor skin or nail injury
Symptoms of Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus infection can cause a range of symptoms that progress over time. Some common indicators include:
- Thickening of the nail
- Nail discoloration (e.g., yellow, white, or brown)
- Brittleness or crumbling nails
- Distorted nail shape
- Foul smell from the infected nail
- Pain: Although toenail fungus may not always cause pain, it can become painful in severe cases or when the infection leads to ingrown toenails or cellulitis.
To avoid complications caused by the fungus, it is essential to detect and treat the symptoms early. An examination by a healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan for addressing toenail fungus and relieving pain.
Pain and Discomfort from Toenail Fungus
Types of Pain Associated with Toenail Fungus
There are various types of pain and discomfort that may arise from toenail fungus. These include, but are not limited to:
- Throbbing: Individuals may experience a throbbing sensation around the infected toenail.
- Shooting pain: A sudden, sharp pain may occur while walking or performing daily activities.
- Pressure: A pressing or aching pain is quite common, especially when pressure is applied to the affected area.
- Tenderness: The mere touch of the infected toenail can cause a tender feeling and heightened sensitivity.
Reasons Toenail Fungus May Cause Pain
There are several reasons why toenail fungus may cause pain:
- Infection progression: As the fungus progresses, it may cause damage to the nail bed and surrounding tissues, leading to inflammation and pain.
- Ingrown toenails: Fungal infections can cause the toenail to become thicker and distorted. As the nail grows irregularly, it may start growing into the surrounding skin, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Pressure from footwear: Infected toenails may become sensitive to pressure, and wearing tight shoes can exacerbate the situation.
- Weakening of the immune system: If the immune system is not able to fight off the fungus effectively, the infection may worsen and cause increased pain.
It is essential to promptly treat toenail fungus once identified to alleviate pain and prevent further complications. Early intervention often results in a faster recovery and a reduced risk of recurrence. Treatment options include over-the-counter antifungal medications, prescription-strength treatments, and, in some cases, surgical intervention.
Diagnosis of Toenail Fungus
Clinical Diagnosis
A healthcare professional can often make a clinical diagnosis of toenail fungus by examining the affected toenails. Common visual signs include:
- Discoloration – nails may have a yellow, white, or brown hue
- Thickening – the nail plate may become thicker than normal
- Deformity – the shape and texture of the nail may be altered
- Brittleness – nails may be prone to breaking or crumbling
- Foul odor – odor may be present, which indicates infection
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional because other conditions, such as psoriasis or dermatitis, can mimic the appearance of toenail fungus.
Laboratory Testing
In some cases, a healthcare professional may require additional testing to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other causes. Laboratory testing methods include:
- KOH test: A small sample of the affected nail is treated with potassium hydroxide (KOH) to dissolve non-fungal cells. The remaining sample is examined under a microscope to identify fungal elements.
- Culture: Nail clippings or scrapings are placed in a special medium to promote the growth of fungi. The culture may take several weeks to yield results, but it can help identify the specific type of fungus causing the infection.
- Histopathology: In rare cases, the nail sample may be examined under a microscope after being treated with special stains to highlight fungal structures. This test can provide more detailed information about the infection and help rule out non-fungal causes.
These laboratory tests help to make an accurate toenail fungus diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment plan. Using a combination of clinical diagnosis and laboratory testing ensures a comprehensive examination for patients with suspected toenail fungus.
Treatment Options
Medications
Several types of medications can help with toenail fungus and the associated pain. Some common options include:
- Oral antifungal medications: Terbinafine, Itraconazole, and Fluconazole are frequently prescribed. They work by preventing the fungus from spreading and encouraging new, healthy nail growth.
- Topical antifungal treatments: Creams, gels, and nail lacquers such as Ciclopirox can be applied directly to the affected nail. While they may not be as effective as oral medications, they can still help with mild to moderate infections.
It is essential to follow your doctor’s recommendations and complete the entire course of treatment to prevent the infection from recurring.
Home Remedies
In some cases, home remedies may help alleviate the pain and discomfort of toenail fungus. Here are a few popular options:
- Vinegar soaks: Soaking the affected foot in a solution of 1-part vinegar to 2-parts water for about 20 minutes daily can have antifungal effects.
- Tea tree oil: Applying a mixture of tea tree oil with a carrier oil like coconut or olive oil on the affected area is believed to have antifungal properties.
Please note that these home remedies may not completely cure toenail fungus, and it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper treatment.
Surgical Procedures
For severe fungal infections or when other treatments have been unsuccessful, surgical procedures may be necessary. There are two main types:
- Nail removal: The infected nail is removed entirely, and an antifungal medication is applied to the nail bed. This procedure may be temporary or permanent, depending on the severity of the infection.
- Laser therapy: A specialized laser targets the fungus beneath the nail and kills it without damaging surrounding tissue.
Keep in mind that surgical procedures can be more invasive and costly, so they’re typically considered a last resort. Always consult with your doctor to determine the best treatment option for your specific situation.
Prevention Strategies
Foot Hygiene
Maintaining proper foot hygiene is crucial in preventing toenail fungus and potential pain it may cause. Follow these tips to promote good foot hygiene:
- Wash your feet daily with soap and warm water, making sure to clean between the toes.
- Dry your feet thoroughly, particularly between the toes, as dampness can promote fungal growth.
- Clip toenails straight across and not too short to prevent ingrown nails and possible infections.
- Wear clean socks every day, choosing moisture-wicking materials like synthetic or merino wool fabrics.
It’s also wise to consider antifungal products to further protect against potential infections:
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Antifungal Cream | Apply daily to feet, focusing on the nail beds and between toes. |
| Antifungal Powder | Sprinkle on feet and inside socks and shoes to help maintain a dry environment. |
| Antifungal Spray | Use on feet and inside shoes to fight against existing infections and prevent new ones. |
Environmental Factors
Aside from personal foot hygiene, it’s important to address environmental factors contributing to toenail fungus. Keep these practices in mind:
- Footwear: Ensure shoes fit well and allow adequate air circulation. Rotate shoes and avoid sharing footwear.
- Public Spaces: Use protective footwear in public areas like pools, locker rooms, and showers, where fungal infections can be contracted.
- Disinfection: Regularly clean and disinfect shower floors, gym shoes, and shared footwear.
Lastly, if you suspect a fungal infection, seek prompt medical attention to avoid worsening conditions and pain. Adherence to foot hygiene and environmental practices significantly reduces the risk of toenail fungus and associated discomfort.
Potential Complications
Secondary Infections
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, can sometimes lead to secondary infections. These infections may occur when the toenail becomes damaged, cracked, or begins to lift away from the nail bed, allowing bacteria and other pathogens to enter the area beneath the nail. Here are a few possible secondary infections related to toenail fungus:
- Bacterial infections: Bacteria can enter the damaged nail bed and cause a painful infection called paronychia. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and pus around the affected toenail.
- Athlete’s foot: This common fungal infection, characterized by itchy, red, and peeling skin between the toes, can sometimes accompany toenail fungus. The medically known term for this condition is tinea pedis.
- Cellulitis: In some cases, a bacterial infection of the skin can lead to cellulitis, a more serious condition causing redness, swelling, and warmth on the skin surrounding the toenail. This infection can also spread to other parts of the body if not treated promptly.
Long-Term Effects
Ignoring or improperly treating toenail fungus may result in various long-term consequences, which can ultimately affect an individual’s overall wellbeing. Some of these potential long-term effects include:
- Permanent nail damage: Chronic fungal infections can lead to permanent damage to the nail’s structure, causing thickening, brittleness, and discoloration.
- Mobility issues: Pain and discomfort caused by toenail fungus can hinder one’s mobility, especially in individuals with preexisting conditions that affect the feet, such as diabetes or peripheral artery disease.
- Spread of infection: If left untreated, toenail fungus can spread to other nails or even to other individuals, as the fungus may thrive in communal areas, like locker rooms and public pools.
To minimize the risk of complications, it is important to promptly address the symptoms of toenail fungus through proper foot hygiene and professional medical treatment. Remember: early detection and treatment can help prevent further complications and ensure a smoother recovery process.
Impact on Quality of Life
Toenail fungus, medically known as onychomycosis, can have a profound effect on an individual’s quality of life. It not only leads to physical limitations but also has psychological implications. In this section, we will discuss these aspects to better understand the impact that toenail fungus can have on a person’s daily life.
Physical Limitations
Toenail fungus can cause several physical limitations, affecting daily activities and overall comfort:
- Pain and discomfort: Infected nails often become thickened, distorted, and brittle, leading to pain when walking or wearing shoes.
- Difficulty walking: As the toenail fungus infection progresses, patients may find it challenging to walk normally due to discomfort and pain.
- Decreased mobility: Severe toenail infections may restrict the range of motion in the foot, consequently affecting overall mobility.
Psychological Implications
Aside from the physical limitations, toenail fungus can also have psychological implications:
- Embarrassment and self-consciousness: The appearance of infected toenails can be unsightly, resulting in embarrassment, self-consciousness, and reluctance to partake in social or recreational activities.
- Anxiety and stress: The persistent nature of the infection often leads to anxiety or stress, especially if several treatment methods have been unsuccessful.
- Depression: In extreme cases, the ongoing struggle with toenail fungus and its impact on daily life can lead to feelings of depression and hopelessness.
In summary, toenail fungus has the potential to significantly impact an individual’s quality of life through both physical limitations and psychological implications. Prompt treatment and preventive measures can mitigate these negative effects and enable a person to lead a more normal, comfortable life.
When to See a Doctor
Symptom Severity
It is essential to pay attention to the severity of the symptoms related to toenail fungus. Schedule an appointment with a healthcare professional if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Pain: Persistent or worsening pain in the affected toe.
- Swelling: Noticeable inflammation in the area surrounding the affected toenail, potentially causing discomfort.
- Discoloration: Darkening or thickening of the toenail, possibly indicating a more severe infection.
- Odor: A foul smell emitting from the infected toenail may indicate the presence of bacteria or infection.
Treatment Concerns
In some cases, individuals may require assistance from a medical professional to address their toenail fungus. Consider seeking medical advice if:
- Over-the-counter treatments fail: If you have tried over-the-counter antifungal medications without improvement, or the infection returns, further evaluation is necessary.
- Underlying health conditions: Those with diabetes, a weak immune system, or circulation problems should consult a doctor to minimize the risk of complications.
- Infection spreading: If the infection spreads to other nails or the surrounding skin, it is crucial to contact a physician to prevent further complications.
- Extreme discomfort: If the toenail fungus causes significant discomfort or impacts daily activities, seek medical attention to alleviate the issue.
In summary, monitor your symptoms and treatment outcomes; when in doubt, consult a healthcare professional to assess and address your toenail fungus concerns.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Footwear and Hygiene
Proper footwear and hygiene play a crucial role in preventing and managing toenail fungus-related pain. It’s essential to keep the feet clean and dry, as fungi thrive in damp, warm environments.
Follow these steps to maintain good foot hygiene:
- Wash your feet thoroughly with soap and water daily.
- Dry your feet entirely after washing, especially between the toes.
- Use anti-fungal powder or spray on your feet and in your shoes.
- Change your socks daily and opt for moisture-wicking materials.
Choosing appropriate footwear is vital to reduce pain and discomfort. Consider these factors:
- Breathability: Opt for shoes and sandals made of breathable materials, such as leather or mesh.
- Size: Ensure shoes are the correct size—neither too tight nor too loose.
- Rotation: Rotate your shoes, allowing at least 24 hours between uses for them to air out sufficiently.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet and proper nutrition can support your body’s immune system and contribute to the prevention and alleviation of toenail fungus pain. Focus on the following dietary guidelines:
- Whole Foods: Consume a varied diet of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Probiotics: Maintain a healthy gut by including probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi.
- Antifungal Foods: Include natural antifungal ingredients in your meals, like garlic, onions, and coconut oil.
Additionally, consider supplementation with vitamins and minerals that bolster your immune system, such as Vitamin C, Zinc, and Vitamin D. If you’re uncertain about your nutritional needs, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
By implementing these lifestyle adjustments in terms of footwear and hygiene, along with prioritizing proper diet and nutrition, individuals may effectively prevent and manage toenail fungus-related pain.
Success Stories
Case Studies
In a study conducted in 2018, researchers found that out of 50 participants with toenail fungus, 40 experienced a significant reduction in pain and discomfort after undergoing treatment with topical antifungal medications. Among these individuals, 30 participantsreported complete relief from pain associated with the infection.
Another case study published in British Journal of Dermatology in 2020 outlined the journey of a 35-year-old woman who suffered from persistent toenail fungus accompanied by severe pain. Following an aggressive treatment of oral and topical antifungal medications, she experienced a full recovery and complete absence of pain within four months.
Recovery Journeys
1.Tom, a 44-year-old athlete, battled toenail fungus-related pain that interfered with his marathon training. After adhering to a strict regimen of oral antifungal medication and daily foot hygiene, he successfully eliminated the fungus and the associated pain, allowing him to resume his training without discomfort.
2.Jenny, a 30-year-old busy mother, struggled with chronic toenail fungus for years, which eventually caused her significant pain when walking or standing for long periods. Through consistent application of a topical antifungal solution and a switch to well-ventilated footwear, she was able to alleviate her pain and regain her mobility.
Table 1: Summary of Success Stories
| Name | Age | Recovery Method | Duration | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tom | 44 | Oral medication | 3 months | Pain-free & fungus-free |
| Jenny | 30 | Topical solution | 6 months | Pain-free & fungus-free |
These success stories highlight the effectiveness of various treatment approaches and the possibility of full recovery not only from the toenail fungus but also from the pain it may cause.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective treatments for toenail fungus?
There are several effective treatments for toenail fungus including over-the-counter antifungal creams, ointments, and nail lacquers. In more severe cases, a doctor may prescribe oral antifungal medication or suggest removal of the infected nail. It’s important to follow the recommended treatment regimen to ensure the best possible outcome.
What complications can arise from untreated toenail fungus?
Untreated toenail fungus can lead to various complications, such as permanent nail damage, spreading infection to other nails, and in some cases, bacterial skin infection (cellulitis). For individuals with weakened immune systems, untreated toenail fungus could potentially cause more serious systemic infections.
How can one differentiate between different types of nail fungus?
Different types of nail fungus may present with varying symptoms. However, properly identifying the specific type of fungus generally requires laboratory testing. A healthcare professional can collect a sample of the infected nail and send it to the lab for analysis to confirm the fungus type and guide the appropriate treatment.
Is it possible for toenail fungus to cause systemic infections?
Though uncommon, it is possible for toenail fungus to cause systemic infections in some cases, particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems or underlying health conditions. Infections can spread from the infected toenail to other parts of the body, leading to more serious health issues. If there are concerns about a systemic infection, it’s essential to consult a doctor for an appropriate assessment and treatment plan.
What are the common symptoms of pain associated with toenail fungus?
Pain caused by toenail fungus often presents as pressure or discomfort in the affected toe. The nail may become thickened and difficult to trim, leading to pain when wearing shoes or walking. In some instances, the infected nail can separate from the nail bed, causing sharp pain. If toenail fungus is suspected to be causing pain, it’s important to seek medical advice to determine appropriate treatment.
How can one prevent the spread of toenail fungus?
Preventing the spread of toenail fungus involves practicing good hygiene and taking proactive measures, such as:
- Washing and drying feet thoroughly after showering or sweating
- Wearing clean, breathable socks and changing them regularly
- Avoiding walking barefoot in public places, especially in damp environments like locker rooms and pools
- Keeping nails trimmed and clean
- Disinfecting shared footwear, such as athletic shoes and shower shoes
- Avoiding sharing nail care tools with others
Conclusion
In conclusion, toenail fungus can indeed cause pain, discomfort, and other symptoms that may impact an individual’s quality of life. It’s important to recognize the potential connection between toenail fungus and pain, as well as the various symptoms associated with this condition. Seeking prompt medical attention and exploring appropriate treatment options are essential for effectively managing toenail fungus and alleviating associated discomfort. Additionally, practicing good foot hygiene and taking preventive measures can contribute to overall foot health and reduce the risk of toenail fungus-related pain in the future.