While toenail fungus itself does not directly cause sepsis, it can lead to sepsis if the infection spreads and becomes severe enough.
People with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes, are at a higher risk for complications from fungal infections. If the fungus penetrates deeper into the skin or bloodstream, it may pave the way for blood infections and the possibility of sepsis.
Understanding how these infections can progress empowers individuals to seek timely medical treatment.
Timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial when dealing with toenail fungus to prevent serious complications.
Recognizing early signs and knowing when to consult a healthcare professional can reduce the likelihood of progression to severe infections.
Taking preventive measures and maintaining proper hygiene can help manage and prevent these infections effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Untreated toenail fungus can lead to more serious infections.
- Early treatment reduces the risk of complications.
- Immediate medical attention is crucial for severe symptoms.
Understanding Toenail Fungus and Onychomycosis
Toenail fungus, often referred to as onychomycosis, is a common condition affecting many individuals. It involves fungal infections that can impact nail appearance and health and might complicate due to other factors.
Causes and Risk Factors
Toenail fungus is mainly caused by various fungi, including dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, which is why wearing sweaty shoes or frequenting damp areas like pools can increase the risk.
Those with a weakened immune system or conditions like diabetes are more prone to these infections. Other risk factors include past injuries to the nail, genetic predisposition, and concurrent fungal infections like athlete’s foot or jock itch.
Prevention often involves maintaining good foot hygiene and keeping nails dry.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
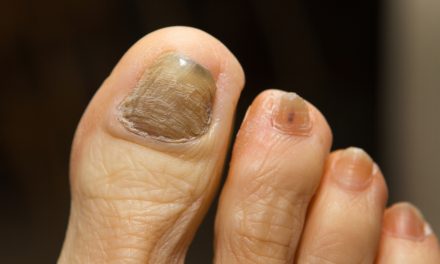
Symptoms of nail fungus may include discoloration, thickening, and crumbling of the nail. The infected nails often turn yellow, brown, or white and might even emit an unpleasant odor.
Pain and discomfort can occur if the infection spreads.
Diagnosing onychomycosis typically involves a visit to a podiatrist or healthcare provider, where they might take a nail sample.
This sample can be analyzed through laboratory tests to identify the specific type of fungus causing the infection.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help in managing and reducing the spread of the infection.
Common Treatments and Medications
Treating toenail fungus often involves oral antifungal medications such as terbinafine and itraconazole. These medications promote new, non-infected nail growth.
Topical treatments include antifungal nail creams and medicated nail polish. For severe cases, a healthcare provider might suggest more advanced treatments like laser therapy or surgical nail removal.
Consistent application and following medical advice are crucial for effective treatment.
Alongside medication, keeping feet clean and dry and regularly washing socks can help minimize reinfection risks.
The Path from Local Infection to Sepsis
Toenail fungus is typically a mild issue but can escalate into severe complications. In certain situations, it may lead to infections spreading beyond the toe, potentially resulting in a medical emergency like sepsis.
Spread of Infection
Toenail fungus starts as a local infection, affecting the nail and surrounding skin. If left untreated, the fungal infection can spread, especially in people with weakened immune systems.
The fungus can break the skin barrier, allowing bacteria to enter. When bacteria invade, they multiply and can move into the bloodstream. The immune system then responds, trying to control the infection.
This response can sometimes go overboard, leading to widespread inflammation.
If the infection reaches the bloodstream, it can become systemic, resulting in sepsis. Sepsis is a serious condition requiring urgent medical attention, as it can cause organ dysfunction.
When Toenail Fungus Becomes a Concern
Toenail fungus often isn’t a significant threat. However, it can be hazardous for individuals with diabetes, poor circulation, or compromised immune systems.
In these cases, the infection is more likely to develop into a severe complication. Changes in nail color, shape, thickness, and pain should not be ignored.
People experiencing persistent symptoms or signs of spreading infection, such as redness or swelling, should seek medical advice.
Addressing the fungus promptly helps prevent the spread of infection and reduces the risk of the infection evolving into sepsis.
Early treatment can safeguard not only the affected toe but also overall health.
Recognizing the Signs of Sepsis
Sepsis is a serious medical condition that requires quick identification and treatment. Recognizing early symptoms like fever and confusion can prevent progression to more severe stages like septic shock, which presents with advanced symptoms such as very low blood pressure and organ failure.
Immediate Symptoms of Sepsis
Early symptoms of sepsis can appear subtly but require immediate attention. A high fever is common, as the body responds to an infection.
Fast breathing and increased heart rate often occur as the body tries to deliver more oxygen.
Confusion or a sudden change in mental status is another key sign, indicating that the brain might not be receiving enough oxygen.
Redness or warmth around an infection site can also be a sign, indicating a localized response to an invading pathogen.
Identifying these early symptoms promptly can be critical in getting the necessary medical attention.
Advanced Sepsis and Septic Shock
As sepsis progresses without treatment, it can lead to septic shock. This advanced stage is characterized by very low blood pressure despite fluid replacement.
Organ dysfunction becomes more evident, with potential severe outcomes like kidney failure.
Patients may experience chills, severe shortness of breath, and significant disorientation. The skin might feel cold due to poor blood flow, which is a stark contrast to the initial redness experienced during early sepsis.
Awareness of these advanced symptoms allows for timely medical intervention, which is essential to improve the chances of recovery and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Risk Factors for Developing Severe Infections
The likelihood of developing severe infections can be influenced by various factors including diabetes and the condition of the immune system. Understanding these aspects can help in assessing the potential risks and in taking preventive measures.
Considerations for Diabetics
Diabetes is a significant risk factor for severe infections. Individuals with diabetes often have reduced blood circulation, especially to the lower extremities. This can make it harder for the body to fight infections effectively.
Diabetic individuals are also prone to foot infections, which may escalate quickly without proper care. In fact, fungal infections of the feet are more common in those with diabetes, potentially leading to complications like cellulitis. The literature highlights that fungal foot infections can compound the risk for cellulitis.
People with diabetes should prioritize foot care and monitoring to prevent complications.
Assessing the Immune System’s Role
The immune system plays a crucial role in fighting off infections. When it is compromised or weakened, the body is more vulnerable to severe infections.
For example, certain medical conditions or treatments like chemotherapy can lower the immune system’s effectiveness.
Chronic conditions such as HIV or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy can increase infection risk.
Evaluating immune function is important for those at risk, helping to guide preventive healthcare decisions.
Both maceration and fungal toe infections can be major concerns for those with weakened immune systems, suggesting a need for vigilant hygiene and healthcare routines to prevent severe infections.
Treatment Protocols for Toenail Fungus and Secondary Infections
Treating toenail fungus involves both antifungal and sometimes antibiotic therapies. In severe cases, surgical interventions may be needed. Each treatment path has its own focus and methods, which are critical for managing and preventing complications.
Antibiotics and Antifungal Therapy
Toenail fungus is primarily treated with antifungal medications, which can be topical or oral.
Topical treatments like ciclopirox nail lacquer are applied directly to the affected nail. Oral medications are another option, offering more comprehensive treatment.
Sometimes, a healthcare provider might prescribe antibiotics if there’s a bacterial infection. This prevents complications like spreading to other areas or causing further health issues.
Keeping an eye on the side effects, such as changes in blood pressure, is vital.
Continuous monitoring and following the podiatrist’s recommendations improve the success of these treatments.
Surgical Interventions and Follow-Up Care
When medications don’t work, surgical intervention might be necessary. The procedure can involve removing part or all of the infected nail, allowing antifungal medicines to reach deeper. This method is often recommended by podiatrists in resistant cases.
Post-surgery, follow-up care involves monitoring for any signs of infection and maintaining nail hygiene.
Regular visits to a healthcare provider ensure the effective management of any complications.
It’s crucial to keep the follow-up appointments, as they help track recovery and ensure that the treatment plan continues to work effectively.
Prevention Strategies and Good Practices
Regular foot care and managing any existing health conditions are crucial in preventing toe fungus and potentially serious complications. Proper hygiene can stop the growth of fungus, while monitoring chronic conditions helps keep the immune system strong.
Hygiene and Foot Care
Keeping feet clean and dry is vital to prevent fungal infections like athlete’s foot. Regular washing with soap and making sure to dry thoroughly, especially between the toes, reduces moisture where fungus thrives.
Wear breathable shoes and change socks daily to avoid damp environments. It’s wise to use antifungal powders or sprays in shoes. Avoid walking barefoot in public areas like locker rooms or pools, where fungus is commonly found.
Consider using a foot scrub or pumice stone to remove dead skin, as fungi can hide in these layers. Regular nail trimming helps keep the nails short, reducing fungal growth.
If a fungal infection is suspected, consult a podiatrist immediately for professional advice.
Managing Chronic Conditions to Reduce Risk
Chronic conditions, like diabetes, compromise the immune system, increasing the risk of infections.
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider help in managing blood sugar levels, reducing the chance of toe fungus becoming a more severe infection.
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients strengthens the immune system.
People with poor circulation should regularly check their feet for injuries or infections. Immediate attention to cuts or lesions prevents complications.
Incorporating exercises as recommended by a healthcare provider can help improve circulation to the feet.
Monitoring chronic foot conditions with professional help ensures they do not escalate into serious health issues.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Sepsis is a serious concern that can arise from untreated infections, including toe fungus. It’s crucial to recognize early warning signs that indicate the infection may be worsening. Timely consultation with a healthcare provider can prevent more severe complications.
Identifying Early Signs of Complications
A fungal infection on the toe might seem minor at first but could escalate quickly. If there is consistent redness, the skin becomes unusually warm, or there is an increase in soreness, it indicates possible complications.
Another warning sign is if the area develops a pus-filled blister. This suggests that the infection may have spread to deeper layers of the skin.
When these symptoms occur, it’s important to act swiftly to prevent further issues.
Swelling and increased pain might also suggest that the infection is not responding to home treatments. Vigilance in observing changes in symptoms can lead to better outcomes.
Engaging with a Healthcare Provider
When symptoms persist or worsen, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential. They can offer medical guidance and determine if the situation needs more intensive treatment.
Doctors may conduct tests to confirm the nature of the infection.
Prompt intervention can stop the progression of the infection and lower the risk of sepsis significantly.
If there is any doubt about the symptoms or if the infection appears to spread, seeking advice from a healthcare professional ensures that proper measures are taken. They might prescribe medications that function more effectively than over-the-counter options.
Understanding the Potential Outcomes and Mortality Rate
Sepsis is a dangerous medical emergency that results from the body’s response to infection. When it becomes severe, it can lead to life-threatening complications like septic shock.
Toe Fungus and Sepsis Risk
Toe fungus, usually mild, rarely leads to serious conditions like sepsis.
In individuals with weakened immune systems, such fungal infections may spread, increasing risks.
Mortality Rates and Statistics
The mortality rate for sepsis depends on the severity of the condition.
For instance, cases involving invasive candidiasis show a 45.9% case fatality ratio.
Other fungal infections linked with sepsis can also have high mortality rates, sometimes reaching 20%.
Key Points:
- Sepsis can result from bacterial and fungal infections.
- A rapid response is crucial to manage it effectively.
- Mortality rates vary based on infection type and patient health.
This information highlights the importance of monitoring fungal infections, especially in those with compromised immune systems, to prevent serious outcomes like sepsis and reduce associated mortality risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Toe fungus can sometimes lead to severe infections like sepsis. It’s crucial to recognize symptoms early and know how such infections can escalate or be treated.
What are the symptoms indicative of fungal sepsis?
Fungal sepsis can cause fever, chills, fast heartbeat, and confusion.
It may also lead to breathing difficulties and low blood pressure. These symptoms can develop quickly and require immediate medical attention.
How can a severe toenail fungal infection lead to serious systemic complications?
A severe toenail fungal infection can spread to other parts of the body, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
The fungus can enter the bloodstream, causing infections in organs and tissues, potentially resulting in life-threatening conditions like sepsis.
What is the mortality rate associated with fungal sepsis?
The mortality rate for fungal sepsis varies, but it can be high, reaching up to 50% in some cases.
Factors influencing this rate include the patient’s overall health and the timeliness of treatment.
How is fungal sepsis typically treated?
Treatment for fungal sepsis often involves antifungal medications administered intravenously.
These medications are chosen based on the specific fungus causing the infection. Supportive care, such as fluid replacement and oxygen therapy, may also be required.
Is it possible for a yeast infection to progress into sepsis?
Yes, a yeast infection can progress to sepsis, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
Yeast can invade the bloodstream and spread to vital organs, requiring immediate medical intervention to prevent complications.
How long can you safely have toenail fungus before it poses a risk of serious health issues?
Toenail fungus may not pose an immediate risk to all individuals, but prolonged untreated infections can eventually lead to more serious complications.
It’s essential to monitor the condition and seek treatment if changes in health occur.