Type 2 diabetes is a growing concern worldwide, but the good news is that it can often be prevented.
Many strategies focus on lifestyle changes that target the main risk factors for this condition.
Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity are crucial steps in diabetes prevention.

Diet plays a significant role in preventing type 2 diabetes.
Choosing a balanced diet with plenty of vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help lower the risk.
Studies also highlight the effectiveness of early pharmacological intervention for those with impaired glucose tolerance, which can help prevent the progression to diabetes.
Monitoring health and staying informed about prediabetes can make a big difference.
Understanding the risk factors and taking proactive steps can delay or prevent the onset of diabetes.
Lifestyle changes, combined with medical advice, empower individuals to manage their health effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented with lifestyle changes.
- Regular exercise and a balanced diet are essential for prevention.
- Early intervention and health monitoring are crucial strategies.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes

Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood glucose. Prediabetes is often a precursor to this condition. Both are linked to insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels.
Defining Diabetes and Its Types
Type 2 diabetes is when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. It is different from Type 1 diabetes, where the body does not produce insulin at all. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, affecting millions worldwide.
Prediabetes occurs when blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. It is important because if left unchecked, prediabetes can progress to Type 2 diabetes.
Early detection and lifestyle changes can help manage and even reverse prediabetes, potentially preventing its progress into full-blown diabetes.
The Role of Insulin Resistance and Blood Sugar Levels
Insulin resistance is a key factor in both prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes. In normal conditions, insulin helps cells use glucose from the blood as energy. When insulin resistance occurs, cells do not respond well to insulin, resulting in higher levels of glucose in the blood.
This elevated blood sugar, or high blood glucose, can lead to various complications over time if not managed effectively.
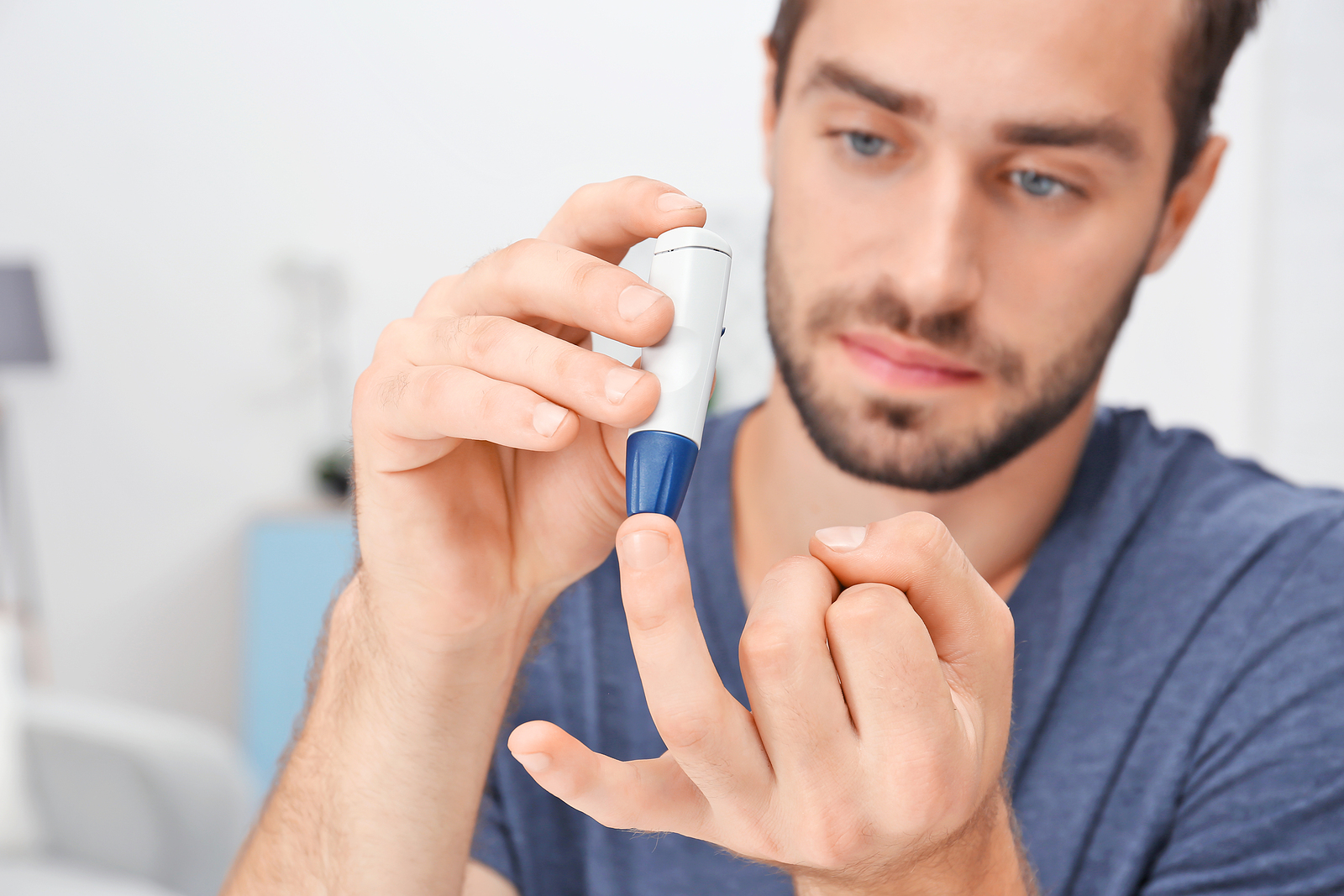
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication can help manage insulin resistance. Regular monitoring of blood glucose is crucial to understanding the body’s response and adjusting treatment approaches as necessary.
Risk Factors and High-Risk Populations

Type 2 diabetes is influenced by various genetic and lifestyle factors, making some groups more susceptible. Certain ethnicities and women who experienced gestational diabetes face a higher risk.
Genetic and Lifestyle Risk Factors
Genetics play a crucial role in determining the likelihood of developing Type 2 diabetes. If a person has family members with the disease, the odds increase significantly.
Lifestyle factors like obesity and being overweight also contribute to the risk, as excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, interferes with how the body uses insulin.
Sedentary behavior further increases the danger. A lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and a decrease in insulin sensitivity. Poor dietary habits, such as consuming high amounts of sugars and processed foods, are common elements that exacerbate the issue.
High-Risk Ethnic Groups and Gestational Diabetes
Certain ethnic groups are at higher risk for Type 2 diabetes. For instance, Asian Americans and Native Americans show higher prevalence rates. Genetic predispositions and lifestyle choices within these communities can fuel this trend.
Gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy, is another risk factor. Women who experience this condition have an increased chance of developing Type 2 diabetes later.
It’s crucial for those with gestational diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight post-pregnancy to reduce the risk. Proper education and awareness can help manage and prevent the onset of Type 2 diabetes in these high-risk populations.
Preventative Strategies for Diabetes Type 2

Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented through effective measures. Focus on lifestyle changes and participation in structured programs can greatly reduce risks associated with developing this condition.
Implementing Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial in preventing type 2 diabetes.
Physical activity plays a major role. Engaging in regular exercise like walking, jogging, or cycling can help maintain a healthy weight.
Healthy eating is another vital aspect. Reducing the intake of sugary and high-fat foods and increasing consumption of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports weight loss and overall health.
This balanced diet helps regulate blood sugar levels, decreasing the likelihood of developing diabetes.
Monitoring weight through a structured plan is essential. Studies show that weight loss of even five to ten percent can lower risks significantly. Building these changes into daily life can effectively prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Involvement in Diabetes Prevention Programs
Participation in a diabetes prevention program is beneficial. These structured programs focus on helping individuals implement and sustain lifestyle changes.
The National Diabetes Prevention Program is a recognized initiative aiming to reduce diabetes cases through proper education and support.
Participants receive guidance on modifying diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
A lifestyle change program involves group sessions led by trained coaches. These programs provide motivation, accountability, and strategies tailored to individual needs, encouraging lasting healthy habits.
By actively engaging in such programs, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Nutrition and Diet’s Role in Prevention

Eating the right kinds of foods can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Focusing on whole foods, managing portion sizes, and reducing added sugar are key strategies.
Designing a Balanced Diabetes-Preventative Diet
A balanced diet focuses on whole grains, fiber-rich foods, and non-starchy vegetables. These foods help regulate blood sugar levels.
Consuming lean proteins such as chicken or fish supports muscle health without adding excess fat.
Including healthy fats like those found in avocados and nuts can be beneficial. They provide energy and help the body absorb vitamins.
Cutting back on sugary drinks and processed foods is crucial. These foods often contain high levels of added sugars and refined grains. Choosing water or unsweetened options is a better choice.
Fruits and vegetables should also be part of the daily meal plan. They provide essential nutrients and vitamins without adding to calorie intake.
Working with a dietitian can help tailor a meal plan to individual needs, ensuring a diet that supports health and diabetes prevention.
Understanding and Managing Portion Sizes
Managing portion sizes can prevent overeating and help maintain a healthy weight.
Using smaller plates or bowls can naturally limit portion sizes. It helps visually control how much is consumed.
Mindful eating is another technique to manage portions. Eating slowly and savoring each bite can prevent overconsumption. Paying attention to hunger cues is essential; eating when hungry and stopping when full is important.
Alcohol also needs moderation as it can add unwanted calories. Setting limits on alcohol intake can assist in maintaining healthy eating habits.
Reading food labels is a helpful tool for understanding portion sizes of packaged foods. Labels provide guidance on serving sizes and nutritional content, leading to better choices.
Physical Activity as a Cornerstone of Prevention
Regular physical activity is crucial in preventing type 2 diabetes. It helps maintain a healthy weight and improves insulin sensitivity. Specific exercises and reducing sedentary behavior are both key components in effective prevention.
Recommended Exercise Types and Durations
To prevent type 2 diabetes, engaging in activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming is beneficial. These exercises are considered moderate-to-vigorous and can significantly impact health.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, spread over multiple days.
Studies have shown that these types of exercises help reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Consistency in performing these activities is important for long-term benefits.
Including strength training exercises, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, twice a week can further enhance the body’s ability to manage blood sugar levels.
Combating Sedentary Behavior
Reducing the amount of time spent sitting has a positive effect on preventing diabetes.
Sedentary behavior is linked to higher blood sugar levels and insulin resistance.
It is important to find ways to break up long periods of sitting by standing, walking, or stretching regularly throughout the day.
Incorporating short walks during breaks or standing while talking on the phone are simple strategies. Adjusting one’s routine to include these small activities can contribute significantly to reducing diabetes risk.
It is about making movement a regular part of daily life, rather than just focusing on structured exercise sessions. Doing so supports weight management and promotes overall health.
Monitoring Health and Understanding Prediabetes
Tracking one’s health is crucial for spotting early signs of prediabetes. Regular health check-ups and risk tests can help monitor potential complications such as heart disease and high blood pressure. These steps are vital for taking action to prevent further health problems.
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups
Regular visits to the healthcare provider play an important role in keeping track of health.
These visits allow for monitoring of blood sugar levels and identifying risk factors for prediabetes. Doctors may perform fasting glucose or A1C tests during these visits.
Detecting high sugar levels early may help prevent major health issues like heart disease or stroke.
Benefits of Regular Check-Ups:
- Early identification of prediabetes
- Monitoring of blood pressure
- Assessment of other health risks
Consequences of Neglecting Check-Ups:
Failing to attend regular visits could lead to delayed diagnosis, increasing the risk of complications like vision loss or other severe health problems.
Utilizing Prediabetes Risk Tests
Prediabetes risk tests are useful tools for assessing the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. These tests consider various factors, including age, weight, family history, and lifestyle choices.
Understanding one’s risk can motivate lifestyle changes to reduce the chances of diabetes.
Components of a Risk Test:
- Family history of diabetes
- Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Blood pressure levels
These tests provide a snapshot of potential health risks. Addressing high-risk factors can lead to preventive measures that make a difference in long-term health outcomes.
Psychosocial and Behavioral Factors
Psychosocial and behavioral factors play a significant role in the management of Type 2 diabetes. Understanding the impact of stress, mental health, and lifestyle choices like smoking and drinking is crucial in preventing this condition.
The Impact of Stress and Mental Health
Chronic stress can negatively influence diabetes management. Stress affects food choices, often leading to higher intake of unhealthy foods.
Additionally, people under stress may have trouble sticking to medication schedules or exercise routines.
Mental health issues such as anxiety or depression can exacerbate these behaviors, making diabetes harder to control.
Support from healthcare providers, along with cognitive-behavioral therapy, may help in reducing stress and improving overall mental health, which is essential for managing diabetes effectively.
Addiction and Lifestyle: Smoking and Drinking
Smoking and drinking are lifestyle habits that can increase the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Smoking damages the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, leading to insulin resistance. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce this risk and improve overall health.
Alcohol consumption, especially in large amounts, can lead to poor blood sugar control.
People with diabetes may benefit from moderating their alcohol intake and focusing on healthier lifestyle choices.
Reducing portion sizes and choosing healthier foods can also help in managing weight and blood sugar levels.
Long-Term Management and Delay of Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes and delaying its onset involves both medications and lifestyle interventions. Medications like metformin, combined with support from lifestyle coaches, can play a vital role in this process.
These strategies focus on reducing risk factors and implementing sustainable changes.
Metformin and Medications in Prevention
Metformin is a medication widely used to help delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
It works by lowering blood sugar levels and improving the body’s response to insulin.
Studies have shown that metformin can be effective in preventing or delaying diabetes in people at high risk, such as those with prediabetes.
Its use alongside lifestyle changes can enhance its effectiveness.
Doctors often recommend metformin as one of the first medications for those at risk.
It is essential to discuss potential side effects and benefits with a healthcare provider before starting any medication. In some cases, other medications may also be considered, but metformin remains the most popular choice for prevention.
It’s a long-term strategy that can significantly contribute to managing diabetes risk.
Lifestyle Coaches and Continued Support
Lifestyle coaches are essential in helping individuals make small, sustainable changes. These changes, like losing weight and staying active, can significantly delay diabetes.
Lifestyle coaches guide individuals through programs focusing on diet and exercise, offering personalized advice and motivation.
A lifestyle change program aims to create lasting healthy habits. Participants work with coaches to set realistic goals, learn stress management techniques, and track their progress.
Continued support and regular check-ins are crucial for maintaining motivation and accountability. With consistent effort, such programs can lead to long-term success in managing and delaying diabetes.
Effective support systems are vital for sustaining these lifestyle changes and reducing diabetes risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
Preventing type 2 diabetes involves making healthy lifestyle choices. Diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes play crucial roles in reducing the risk. Understanding these aspects can provide actionable steps for those looking to prevent diabetes.
How can I prevent diabetes naturally?
Eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity are key to preventing type 2 diabetes.
Maintaining a healthy weight and managing stress effectively also contribute to lowering the risk of developing the condition.
What are the dietary choices that help in preventing type 2 diabetes?
Choosing foods high in fiber and low in refined sugars can help. Incorporating whole grains, fruits, and vegetables into your diet is beneficial.
Consuming healthy fats, such as those found in nuts and avocados, may also aid in prevention.
Can regular exercise reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes?
Yes, regular exercise helps the body use insulin more efficiently, reducing the risk of developing diabetes.
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity, like walking or cycling, each week is recommended.
What lifestyle modifications can help prevent diabetes in individuals with a family history?
Managing weight through healthy eating and exercise is crucial for those with a family history of diabetes.
Regular health screenings and monitoring blood sugar levels can also provide early warning signs and help prevent its onset.
Are there any proven strategies to stop diabetes before it starts?
Lifestyle changes such as increased physical activity and healthier eating choices are proven strategies for diabetes prevention.
Some studies, like those found in the Diabetes Prevention Program, highlight the effectiveness of these interventions.
What are the main risk factors for type 2 diabetes and how can they be mitigated?
Risk factors include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and poor diet. Addressing these through regular exercise, weight management,, and a nutritious diet can significantly lower the risk.
High-risk individuals might benefit from specific preventive programs.