Toenail fungus and neuropathy are two health issues that can affect your feet. Many people wonder if there’s a link between them. While toenail fungus doesn’t directly cause neuropathy, it can lead to problems for those who already have nerve damage.

People with diabetes often deal with both of these foot problems. Diabetic neuropathy can make it hard to feel injuries or infections in the feet. This means a fungal nail infection might go unnoticed and get worse over time.
Fungal nail infections can cause the nail to thicken or break. This can hurt the skin around it. For someone with neuropathy, small injuries from a thick, infected nail might not be felt right away. Treating toenail fungus is important to avoid these issues.
Key Takeaways
- Toenail fungus doesn’t directly cause neuropathy but can worsen foot problems in people with nerve damage.
- People with diabetes need to watch for both fungal infections and neuropathy in their feet.
- Early treatment of toenail fungus helps prevent complications, especially for those with nerve issues.
Understanding Toenail Fungus
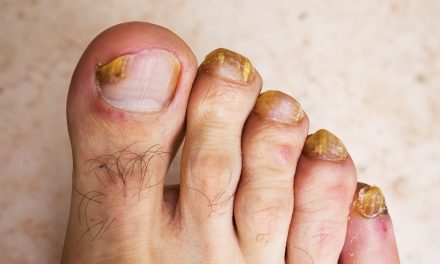
Toenail fungus is a common condition that affects many people. It can cause discoloration, thickening, and crumbling of the nails. This infection can be stubborn and may take time to treat effectively.
Causes of Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is caused by various types of fungi. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments. People often get toenail fungus from walking barefoot in public areas like locker rooms or swimming pools.
Diabetic patients are at higher risk due to reduced blood flow to the feet. Other risk factors include:
- Age (older adults are more susceptible)
- Sweaty feet
- Tight shoes
- Weakened immune system
- Athlete’s foot
Poor foot hygiene can also contribute to fungal growth. Keeping feet clean and dry is key to preventing infection.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Toenail fungus often starts as a small white or yellow spot under the nail. As it spreads, it can cause:
- Nail discoloration (yellow, brown, or white)
- Thickening of the nail
- Brittle or crumbly nails
- Misshapen nails
- Foul odor
Doctors diagnose toenail fungus by examining the affected nails. They may take nail clippings or scrape debris from under the nail for lab testing. This helps identify the specific type of fungus causing the infection.
Early detection is important for effective treatment. If left untreated, the infection can spread to other nails or even the surrounding skin.
Neuropathy Basics
Neuropathy is nerve damage that can affect different parts of the body. It has several types and causes various symptoms that impact daily life.
Types of Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common type. It affects nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. This kind often damages nerves in the feet and hands.
Autonomic neuropathy impacts involuntary body functions. These include heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion.
Focal neuropathy affects single nerves, usually in the head, torso, or leg. It can cause sudden weakness or pain.
Proximal neuropathy damages nerves in the hip, buttock, or thigh. This type is less common but can be very painful.
Common Symptoms
Numbness and tingling in hands or feet are typical signs of neuropathy. Many people describe a “pins and needles” feeling.
Sharp, burning pain is another frequent symptom. This pain may be constant or come and go.
Muscle weakness can occur, making it hard to do simple tasks. Some people have trouble buttoning shirts or walking.
Changes in sensation are common. People might not feel temperature changes or pain in affected areas.
Balance problems can develop due to lost feeling in the feet. This increases the risk of falls.
Digestive issues, such as nausea or constipation, may happen with autonomic neuropathy.
The Connection Between Toenail Fungus and Neuropathy
Toenail fungus and neuropathy can be linked in people with diabetes. This connection involves risk factors and potential complications that may affect foot health.
Scientific Evidence
Diabetic neuropathy and peripheral arterial disease can make people more prone to toenail fungus. Nerve damage may reduce sensation in the feet, making it hard to notice fungal infections.
Fungal infections can worsen existing foot problems in diabetic patients. This can lead to more serious issues if left untreated.
Studies show that people with diabetes often have both toenail fungus and nerve problems in their feet. This combination can increase the risk of foot ulcers and other complications.
Risk Factors
Diabetes is a major risk factor for both toenail fungus and neuropathy. High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and weaken the immune system.
Poor blood flow to the feet, common in diabetes, can make it harder for the body to fight fungal infections. This creates an ideal setting for fungi to grow.
Sensory neuropathy can mask pain or discomfort from fungal infections. This may delay treatment and allow the infection to spread.
Wearing tight shoes or having sweaty feet can also increase the risk of toenail fungus. These conditions create a warm, moist environment that fungi love.
Impact of Toenail Fungus on Mental and Mind Health
Toenail fungus can affect more than just physical health. It may also have a significant impact on a person’s mental and mind health.
Many people with toenail fungus feel embarrassed about the appearance of their nails. This can lead to lowered self-esteem and reduced confidence in social situations.
The persistent nature of fungal infections can cause frustration and stress. Patients may feel discouraged if treatments take a long time to work or if the infection keeps coming back.
Some individuals avoid activities they once enjoyed, like swimming or going barefoot, due to their nail condition. This social withdrawal can negatively affect mental health.
Chronic health issues like toenail fungus may increase the risk of anxiety or depression in some people. The ongoing worry about the infection spreading or getting worse can be mentally draining.
Sleep problems might occur if a person spends time worrying about their condition at night. Poor sleep can then further impact overall mental well-being.
It’s important to note that while toenail fungus itself doesn’t directly cause mental health issues, the stress of dealing with it can take a toll. Seeking proper treatment and support can help manage both the physical and mental aspects of this condition.
Complications of Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus can lead to various issues beyond the nail itself. These problems can affect both physical health and emotional well-being.
Physical Complications
Fungal nail infections can cause pain and discomfort when walking or wearing shoes. The infected nail may thicken and become brittle, making it hard to trim. This can lead to ingrown toenails and cuts on nearby skin.
For people with diabetes, toenail fungus is more serious. It can increase the risk of foot ulcers and infections. These issues are harder to heal due to poor blood flow and nerve damage in diabetic feet.
In rare cases, severe fungal infections may spread to other parts of the body. This can happen if the immune system is weak. It’s important to treat toenail fungus early to avoid these risks.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Toenail fungus can affect a person’s mental health. Many people feel embarrassed about the look of their nails. They may avoid activities that show their feet, like swimming or going barefoot.
This shame can lead to social isolation and low self-esteem. Some people may feel anxious in social situations or when dating. The long-term nature of fungal infections can also cause frustration and stress.
These feelings can impact daily life and relationships. It’s important to address both the physical and emotional aspects of toenail fungus for complete treatment.
Treatment Options for Toenail Fungus
Treating toenail fungus can be done with medications, home remedies, and preventative steps. The right approach depends on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health.
Medications
Oral antifungal drugs are often the first choice for treating toenail fungus. Terbinafine is a common option that can be effective and may have fewer side effects than other treatments. It’s usually taken for 6 to 12 weeks.
Topical medications are another option. These are applied directly to the infected nail. They work best for mild to moderate infections. Nail polishes containing antifungal medicine can be painted on the nail daily.
In some cases, a doctor might prescribe a combination of oral and topical treatments. This can help attack the infection from multiple angles.
Alternative and Home Remedies
Some people try natural remedies for toenail fungus. Tea tree oil is a popular choice. It has antifungal properties and can be applied to the nail with a cotton swab.
Vinegar foot soaks are another home remedy. Mix one part vinegar with two parts warm water and soak the feet for 15-20 minutes daily.
Oregano oil is thought to have antifungal properties. It can be mixed with a carrier oil and applied to the affected nail.
While these remedies might help, they often take longer to work than medications. They may be best for mild cases or as a supplement to medical treatment.
Preventative Measures
Preventing toenail fungus is key to avoiding future infections. Keeping feet clean and dry is crucial. After washing, dry feet thoroughly, especially between the toes.
Wear breathable shoes and change socks daily. Avoid walking barefoot in public areas like locker rooms or pools.
Use antifungal sprays or powders in shoes. This can help prevent fungus from growing.
Trim nails regularly and keep them short. This reduces the space where fungus can grow.
For people with diabetes, proper foot care is extra important. Regular check-ups with a podiatrist can help catch and treat infections early.
Managing Neuropathy
Neuropathy from toenail fungus can be managed through medical treatments and lifestyle changes. These approaches aim to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Medical Treatments
Doctors may prescribe medications to ease nerve pain. Common options include gabapentin, pregabalin, and duloxetine. These drugs target the nervous system to reduce pain signals.
Topical treatments like lidocaine patches or capsaicin cream can provide local relief. They work by numbing the skin or blocking pain signals.
For severe cases, doctors might suggest nerve blocks. This involves injecting numbing medicine near affected nerves.
Physical therapy can help improve strength and balance. A therapist may teach exercises to reduce fall risk and enhance mobility.
Lifestyle Changes
Diet plays a key role in managing neuropathy. Eating a balanced diet rich in B vitamins, especially B12, can support nerve health. Foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, and fortified cereals are good sources.
Regular exercise can improve blood flow and reduce pain. Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling are often recommended.
Quitting smoking is crucial. Tobacco use can worsen nerve damage and slow healing.
Proper foot care is essential. This includes:
- Daily foot checks
- Wearing comfortable, well-fitting shoes
- Keeping feet clean and dry
- Trimming toenails carefully
Stress management techniques like meditation or yoga may help. They can ease tension and improve mental health, which often suffers due to chronic pain.
Prevention Strategies for Toenail Fungus and Neuropathy
Preventing toenail fungus and neuropathy requires a two-pronged approach. A balanced diet and proper foot care are key to reducing the risk of these conditions.
Diet and Nutrition
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in preventing toenail fungus and neuropathy. Eating foods rich in vitamins and minerals helps boost the immune system and promote overall foot health.
Include foods high in vitamin B12, such as eggs, fish, and lean meats. This vitamin is essential for nerve health and function.
Increase intake of foods with antioxidants like berries, leafy greens, and nuts. These help fight inflammation and protect against nerve damage.
Limit sugar and refined carbohydrates. High blood sugar can weaken the immune system and make it easier for fungal infections to take hold.
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. This helps flush out toxins and keeps skin healthy.
Foot Care Tips
Proper foot care is essential to prevent both toenail fungus and neuropathy. Regular cleaning and inspection can catch problems early.
Wash feet daily with soap and water. Dry thoroughly, especially between toes.
Trim toenails straight across and file down thickened areas. This prevents skin injury that could lead to infections.
Wear clean, dry socks made of moisture-wicking materials. Change them daily or more often if feet get sweaty.
Choose shoes that fit well and allow feet to breathe. Avoid tight shoes that can cause pressure points or restrict circulation.
Use antifungal powder or spray in shoes and on feet to prevent fungal growth.
Inspect feet daily for cuts, blisters, or signs of infection. This is especially important for those with diabetes or existing neuropathy.
The Importance of Early Detection
Catching toenail fungus early can prevent serious complications. Quick action helps stop the infection from spreading and reduces the risk of long-term damage.
Regular Screenings
Regular foot checks are key for spotting toenail fungus. Look at your toes and nails often, at least once a week. Pay close attention to any changes in color, shape, or texture.
Use a mirror to check hard-to-see areas. Good lighting helps too. If you have trouble seeing your feet, ask a family member or caregiver to help.
People with diabetes need extra care. Their risk of foot problems is higher. They should check their feet daily and see a doctor regularly.
Recognizing Early Signs
Early signs of toenail fungus are easy to miss. Watch for:
- Yellow or white spots on nails
- Thickened or misshapen nails
- Brittle, crumbly, or ragged nails
- Dull nails with no shine
- Dark color from debris buildup
- Slightly smelly nails
Don’t ignore these signs. Early treatment works best. It stops the fungus from spreading to other nails or skin.
If you see any changes, talk to a doctor. They can check if it’s really fungus. Some other foot problems look similar. A proper diagnosis ensures the right treatment.
Navigating the Health System
Getting proper care for toenail fungus and neuropathy requires working with the right doctors and understanding costs. Patients need to know how to find specialists and navigate insurance coverage.
Finding the Right Specialist
Diabetic foot complications often require specialized care. Patients should start by seeing their primary care doctor for an initial assessment. The doctor may then refer them to a podiatrist or dermatologist.
Podiatrists focus on foot health and can diagnose fungal infections. Dermatologists specialize in skin and nail conditions. For neuropathy concerns, a neurologist may be needed.
Patients can ask their primary doctor for recommendations. They can also search online for specialists in their area. Reading reviews and checking credentials helps find experienced doctors.
Insurance and Cost Considerations
Treatment costs vary based on the type of care needed. Most health insurance plans cover medically necessary treatments for toenail fungus and neuropathy. However, coverage levels differ.
Patients should:
- Check their policy details
- Ask about copays and deductibles
- Get pre-authorization if required
Some medications for fungal infections can be expensive. Generic options may lower costs. For neuropathy, insurance typically covers doctor visits and tests.
Uninsured patients can ask about cash discounts or payment plans. Some clinics offer sliding scale fees based on income. Comparing prices at different providers may find more affordable options.
Long-Term Outlook
Living with toenail fungus and neuropathy can be challenging. The right care and support make a big difference in managing these conditions over time.
Living with Toenail Fungus and Neuropathy
Toenail fungus often needs long-term treatment. People may need to take medicine for months or even a year. Even after treatment, the fungus can come back. This means ongoing foot care is key.
For those with neuropathy, regular foot checks are vital. They should look for any cuts, sores, or changes in their feet daily. Good blood sugar control helps slow nerve damage in diabetics with neuropathy.
Proper footwear is a must. Shoes that fit well and breathe can help prevent both fungal growth and foot injuries. Keeping toenails trimmed and feet clean and dry also helps.
Support and Resources
Getting support is crucial for mental health when dealing with ongoing foot issues. Support groups can offer tips and emotional help. These groups exist both online and in person.
Doctors play a big role in long-term care. Regular check-ups with a podiatrist or dermatologist are important. They can spot problems early and adjust treatment as needed.
Many hospitals have special foot clinics for people with diabetes. These clinics offer expert care and education. They teach patients how to care for their feet at home.
Online resources can also help. Websites of health organizations often have tips for foot care and living with neuropathy. Some offer tools to track symptoms and treatment progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
Toenail fungus and neuropathy are complex conditions that can affect foot health. Many people have questions about their connection, symptoms, and treatment options.
Can a fungal infection in the toenails lead to peripheral neuropathy?
Toenail fungus itself does not directly cause neuropathy. However, both conditions can occur together, especially in people with diabetes or weakened immune systems.
Fungal infections may create openings in the skin that allow bacteria to enter. This can lead to infections that might damage nerves over time.
What are the symptoms of neuropathy in the feet?
Neuropathy in the feet often causes numbness, tingling, or burning sensations. People may feel pins and needles or sharp pains in their feet.
Some experience decreased sensitivity to temperature or touch. Others may have trouble feeling their feet when walking.
Is there a risk of severe complications, such as death, from peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy itself is not typically life-threatening. However, it can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
People with neuropathy may not notice injuries to their feet. This can result in infections or ulcers that are hard to heal.
Could receiving a pedicure result in nerve damage in the feet?
Pedicures done properly are generally safe. However, aggressive cleaning or cutting of nails and skin can potentially cause injury.
People with existing neuropathy or diabetes should be extra careful. They may not feel pain from small cuts that could become infected.
What treatment options are available for neuropathy in the lower extremities?
Treatment for neuropathy depends on its cause. Medications can help manage pain and other symptoms.
Physical therapy and special footwear may improve mobility and prevent further damage. Controlling blood sugar is crucial for people with diabetes.
Are there other medical conditions commonly associated with toenail fungal infections?
Toenail fungus often occurs alongside other foot problems. These may include athlete’s foot, plantar fasciitis, or ingrown toenails.
People with diabetes or circulatory issues are more likely to develop fungal nail infections. These conditions can also make infections harder to treat.
Conclusion
Toenail fungus and neuropathy are separate conditions. While they can occur together, one does not directly cause the other.
People with diabetes have a higher risk of both issues. Sensory neuropathy can make it harder to notice foot problems, including fungal infections.
Treating toenail fungus is important. Left unchecked, it may lead to more serious infections. Some treatments can have side effects, but these are usually mild.
Regular foot checks are key for those with diabetes or neuropathy. This helps catch problems early. Proper foot care also helps prevent issues.
Seeing a doctor for any foot concerns is smart. They can diagnose the problem and suggest the best treatment plan.
With proper care and treatment, both toenail fungus and neuropathy can be managed. This helps prevent more serious problems down the road.