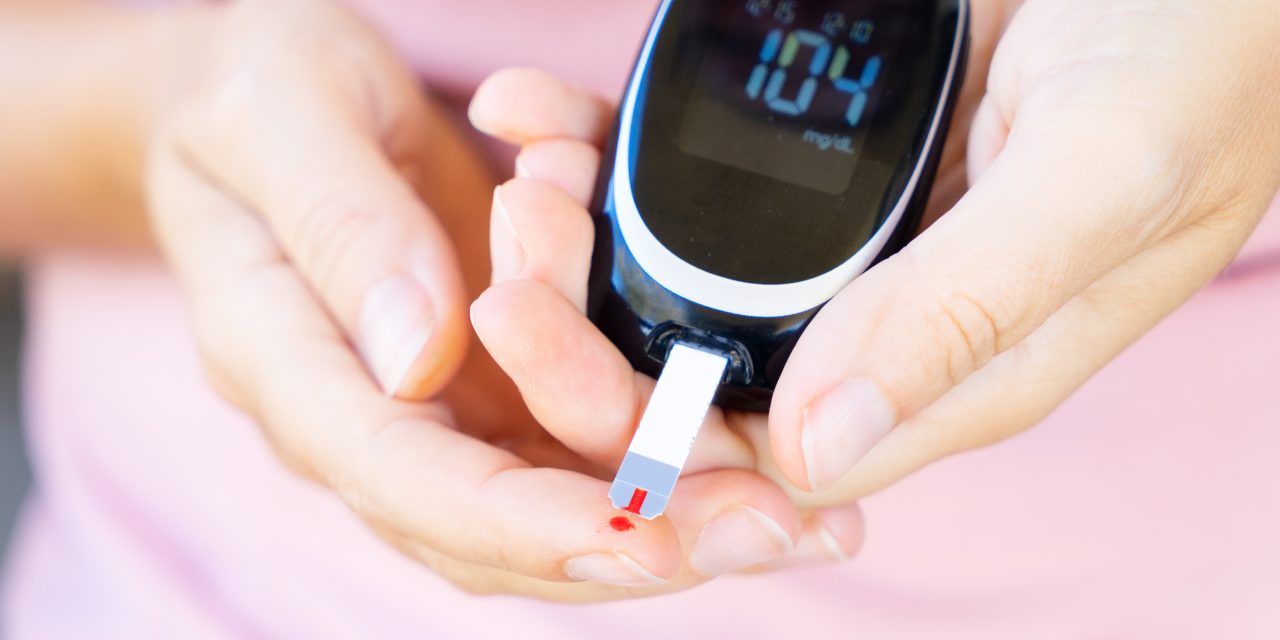
For those managing diabetes, or anyone interested in how body weight affects health, understanding the link between weight loss and blood sugar can be crucial.
Weight loss often plays a significant role in improving various health metrics, particularly for individuals dealing with diabetes or high blood sugar.
Losing excess weight can lead to lower blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health. This connection offers hope for better managing diabetes and reducing complications.
When someone loses weight, their body often uses insulin more effectively, which can lead to improved blood sugar control.
Reducing excess body fat, especially abdominal fat, helps reduce insulin resistance. This not only supports healthier blood sugar levels but can also decrease the risk of further complications.
Incorporating a balanced diet and regular physical activity can significantly aid in managing weight and blood sugar levels.
A structured plan that includes balanced nutrition and consistent exercise can make a remarkable difference in one’s health journey. Such strategies, when combined with medical advice, can offer sustainable benefits.
Key Takeaways
- Weight loss can improve blood sugar control by enhancing insulin sensitivity.
- Proper diet and exercise are essential for managing weight and blood sugar.
- Working with healthcare professionals can optimize a personalized plan.
Understanding Blood Sugar and Its Relation to Weight
Excess weight often affects blood glucose levels, making it harder to maintain healthy blood sugar. Insulin plays a crucial role in this process, as it helps regulate glucose levels in the body.
The Role of Insulin in Blood Sugar Management
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas. It plays an essential role in controlling blood sugar.
When a person eats, carbohydrates from food break down into glucose. Insulin helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream so it can be used for energy.
Without enough insulin, or if the body doesn’t respond to it properly, glucose builds up in the blood. This leads to high blood sugar levels.
Insulin resistance is a condition where the body’s cells do not respond well to insulin. This often occurs in individuals with excess weight or obesity.
Managing insulin effectively is vital for keeping blood sugar stable.
Reducing body weight can improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use glucose more efficiently. This reduces the risk of high blood sugar and related health issues.
How Excess Weight Affects Blood Glucose Levels
Excess weight can lead to higher blood glucose levels. Fat cells, especially those stored around the abdomen, can become large and less responsive to insulin. This increases the risk of insulin resistance.
When the body becomes resistant to insulin, it needs more to manage blood sugar levels. The pancreas struggles to meet this demand. As a result, blood glucose levels rise. This is often seen in individuals with obesity.
Reducing weight can decrease the size and improve the function of fat cells. It also helps the body respond better to insulin, lowering blood glucose levels. This highlights the importance of weight management in controlling blood sugar and reducing health risks.
The Impact of Weight Loss on Blood Sugar Control
Losing weight can have important effects on blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with diabetes. It helps reduce insulin resistance and improves the function of the pancreas, both of which are crucial for controlling blood sugar.
Reducing Insulin Resistance
Weight loss can significantly lower insulin resistance. When body weight decreases, cells respond better to insulin, allowing glucose to enter cells more easily. This process helps to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
The reduction in fat around organs also plays a role. Less fat means less inflammation, which minimizes insulin resistance. This is crucial for those with type 2 diabetes, as it aids in better glucose control.
Exercise and a balanced diet can enhance these effects, further improving insulin sensitivity.
Maintaining a consistent weight loss plan helps in achieving long-term blood sugar stability.
Improvement in Pancreatic Function
Weight loss can lead to better pancreatic function. The pancreas is responsible for releasing insulin, a hormone that controls blood sugar levels.
Losing weight reduces the stress on the pancreas, enabling it to release insulin more effectively.
In people with obesity-related diabetes, excessive fat hinders the pancreas’s ability to function optimally. Shedding extra pounds can relieve this burden, improving insulin production and release.
Better pancreatic function also means more efficient glucose regulation, which is vital for preventing long-term complications associated with high blood sugar. Regular weight management efforts support healthy pancreatic activity over time.
Dietary Strategies for Managing Blood Sugar
Adjusting diet can play a significant role in controlling blood sugar levels. Choosing the right foods and maintaining balanced meals are important steps.
Balanced Carbohydrate Intake
Carbohydrates have a direct impact on blood sugar. Choosing the right type and quantity is necessary.
Focus on whole grains, such as brown rice and oats. These are processed slowly and can help avoid spikes in sugar levels.
Fruits and vegetables, though containing carbs, offer essential vitamins and minerals. Consuming these in moderation is recommended.
Opt for lower glycemic index (GI) foods like berries and leafy greens, which have less impact on blood sugar levels. Managing portion sizes also aids in controlling sugar levels.
Incorporating Fiber and Lean Protein
Adding fiber and lean protein to meals can help keep blood sugar steady.
Fiber slows down digestion, which can prevent sharp increases in sugar levels. Foods high in fiber include vegetables, legumes, and whole grains like quinoa and barley.
Lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, and tofu, are vital for meal balance. They help in muscle repair and satisfy hunger without raising blood sugar.
Including protein in every meal helps maintain stable energy levels throughout the day. Pairing fiber and protein with healthy fats, like avocados or nuts, can aid in further balancing blood sugar.
Exercise’s Role in Weight and Blood Sugar Management
Engaging in regular exercise plays a significant role in managing body weight and blood sugar levels. Both aerobic and resistance training provide various benefits that can support overall health and help in burning fat.
Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and managing weight.
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to use glucose more effectively. This helps reduce blood sugar levels and can be particularly beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes.
A study by the American Diabetes Association highlights how exercise reduces cardiovascular risk factors and supports weight loss.
Exercise also aids in weight management by increasing the body’s metabolism, leading to more efficient fat burning.
Regular workouts contribute to a healthier body composition, decreasing fat mass while preserving muscle mass. These factors combined can help individuals maintain a healthy weight and improve their overall metabolic profile.
Types of Exercises Recommended
Various types of exercises can effectively help manage weight and blood sugar levels.
Aerobic exercises like walking, running, and cycling are highly recommended. These activities are ideal for improving cardiovascular health and enhancing the body’s ability to use insulin. They also aid in weight loss by burning calories and reducing body fat.
Resistance training should also be included in a fitness routine.
Lifting weights or performing bodyweight exercises, such as push-ups and squats, helps build muscle. Increased muscle mass boosts metabolism, leading to better weight control.
Incorporating both aerobic and resistance exercises ensures a balanced approach to improving health and managing blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle Modifications for Sustainable Health
Lifestyle changes such as improving sleep habits and adopting a Mediterranean diet can greatly contribute to better health. These strategies focus on mental health and the benefits of eating whole foods.
Importance of Sleep and Stress Management
Quality sleep is crucial for maintaining good health. It helps regulate hormones that control hunger and insulin, which can impact both weight and blood sugar levels.
Insufficient sleep often leads to increased stress, which can negatively affect mental health.
Managing stress effectively is another key component. Stress can lead to unhealthy eating habits, which may disrupt blood sugar levels.
Techniques like mindfulness and relaxation exercises can help reduce stress. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can improve sleep quality, which supports metabolic health.
Adopting a Mediterranean Diet Approach
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. This eating pattern is known for its health benefits, including improved blood sugar control and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Healthy fats from sources like olive oil and nuts are also a mainstay of this diet.
Incorporating this diet involves replacing processed foods with unprocessed alternatives. Increased consumption of plant-based meals and reduced sugar intake can promote better health outcomes.
By focusing on a balanced diet rich in nutrients, individuals can support their metabolic health and possibly lower blood sugar levels.
Medication and Medical Interventions
In managing diabetes, diet and exercise play a crucial role. However, medication and medical interventions become necessary when lifestyle changes alone don’t suffice. These treatments help control blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
When Diet and Exercise Are Not Enough
For many with type 2 diabetes, a healthy lifestyle may not be sufficient to maintain normal blood sugar levels. In such cases, medication becomes essential.
Doctors often prescribe oral medications like metformin, which decreases the amount of glucose produced by the liver. It also enhances insulin sensitivity.
Insulin therapy might be recommended when blood sugar levels remain uncontrolled with oral medications. Different insulin types, including rapid-acting and long-acting, can be customized to suit individual needs.
Cholesterol-lowering medications and blood pressure treatments might also be included to manage overall health risks.
Understanding Diabetes Medication and Insulin Therapy
Diabetes management frequently involves a combination of different medications. Each medication works in a unique way.
For instance, sulfonylureas increase insulin production in the pancreas, while SGLT2 inhibitors help the kidneys remove glucose from the bloodstream.
Insulin therapy can be intricate. It requires understanding how different types work within the body.
Patients must follow prescribed regimens carefully and monitor glucose levels regularly to avoid complications.
Doctors may adjust medication types and dosages based on an individual’s response to treatment. This personalized approach ensures effective blood sugar control. It also reduces the risk of serious health issues associated with diabetes.
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment Plans
Monitoring blood sugar levels is important in managing diabetes. Using continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) can help track glucose levels in real time. Additionally, A1C testing provides a longer-term view of glucose control, making both tools essential for effective diabetes management.
Utilizing Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM)
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) help people with diabetes track their blood sugar levels throughout the day. These small devices give real-time updates on glucose levels, which can help in adjusting treatment plans.
By wearing a CGM, patients can get alerts when their blood sugar is too high or too low.
These alerts assist in quickly addressing any issues that arise. Using CGMs can help in making informed decisions about diet and exercise. Adjustments to medication can also be made based on the data provided by the CGM.
This personalized data allows for better management of diabetes by keeping glucose levels within the target range.
The Importance of A1C Testing
A1C testing measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. This test is crucial for understanding long-term glucose control.
Regular A1C tests can help adjust treatment plans effectively. High A1C results indicate a need for changes in diet, exercise, or medication.
A1C testing is a standardized way of monitoring diabetic control and is recommended about every three to six months.
By reviewing A1C results, healthcare providers can make informed decisions on whether to adjust insulin doses or other medications. Understanding A1C levels is vital for reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Potential Complications of High Blood Sugar and Obesity
High blood sugar and obesity can lead to various health issues. Heart disease is a significant risk because high blood sugar can damage blood vessels.
This damage increases the risk of blockages, which can lead to heart attacks or strokes. Obesity and high blood sugar also impact the nerves.
This condition, known as neuropathy, can cause numbness or pain, especially in the feet and hands. Nerve damage is common in people with prolonged high blood sugar levels.
Kidney disease is another complication. High sugar levels force the kidneys to work harder, leading to possible kidney damage or failure over time. People with obesity are at a higher risk for this progression. Vascular damage affects the circulatory system, causing poor blood flow.
This issue can result in slow wound healing and may contribute to various complications, including disease progression in diabetes. Sleep apnea is frequently seen in individuals with obesity.
This condition can worsen both obesity and diabetes, creating a complex cycle of health issues. Treating sleep apnea may help improve overall health outcomes. Those with high blood sugar who are not yet diabetic may be in a state called prediabetes.
Recognizing and managing this early can prevent further health complications. Effective management of high blood sugar and obesity involves lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, to reduce these risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Losing weight can play a significant role in managing blood sugar levels and controlling diabetes. This section addresses how weight loss affects blood sugar, HbA1c results, and diabetes management.
Does losing weight have an impact on blood sugar levels?
Losing weight can help lower blood sugar levels. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, reducing body weight may lead to improved insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to manage glucose.
According to research, weight loss often results in lower fasting blood sugar levels, contributing to overall better glucose control.
Can weight loss improve hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test results?
Weight loss has the potential to improve HbA1c test results. A study found that interventions involving a low-calorie diet helped in reducing HbA1c levels.
As individuals lose weight, they often experience a decrease in these levels, indicating improved long-term blood sugar control.
What is the relationship between weight loss and type 2 diabetes management?
Weight loss is closely linked to type 2 diabetes management. It can lead to better regulation of blood sugar and may reduce the need for diabetes medications.
Studies, such as those on obese persons with type 2 diabetes, show that losing weight helps many individuals achieve better control over their condition.
How much weight loss is generally required to have an effect on diabetes reversal?
Generally, a weight loss of about 5% to 10% of body weight can significantly impact diabetes management and potential reversal. This amount of weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels, thereby aiding in better management of diabetes symptoms and sometimes leading to disease remission.
Why might blood sugar levels increase despite weight loss in some diabetic individuals?
In some cases, blood sugar levels may increase despite weight loss. This can be due to factors such as stress, changes in diet or medications, or other underlying health conditions that affect insulin and blood sugar regulation.
Continuous monitoring and consultation with healthcare providers are essential to address these challenges.
Is there a difference between intentional and unintentional weight loss in the context of diabetes?
Intentional weight loss, achieved through diet and exercise, is usually beneficial for managing diabetes.
Unintentional weight loss, on the other hand, could indicate uncontrolled blood sugar or other health issues.
People with diabetes experiencing unintentional weight loss should consult their healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and make necessary adjustments.