Toe fungal infections, known as onychomycosis, are common and can affect anyone.
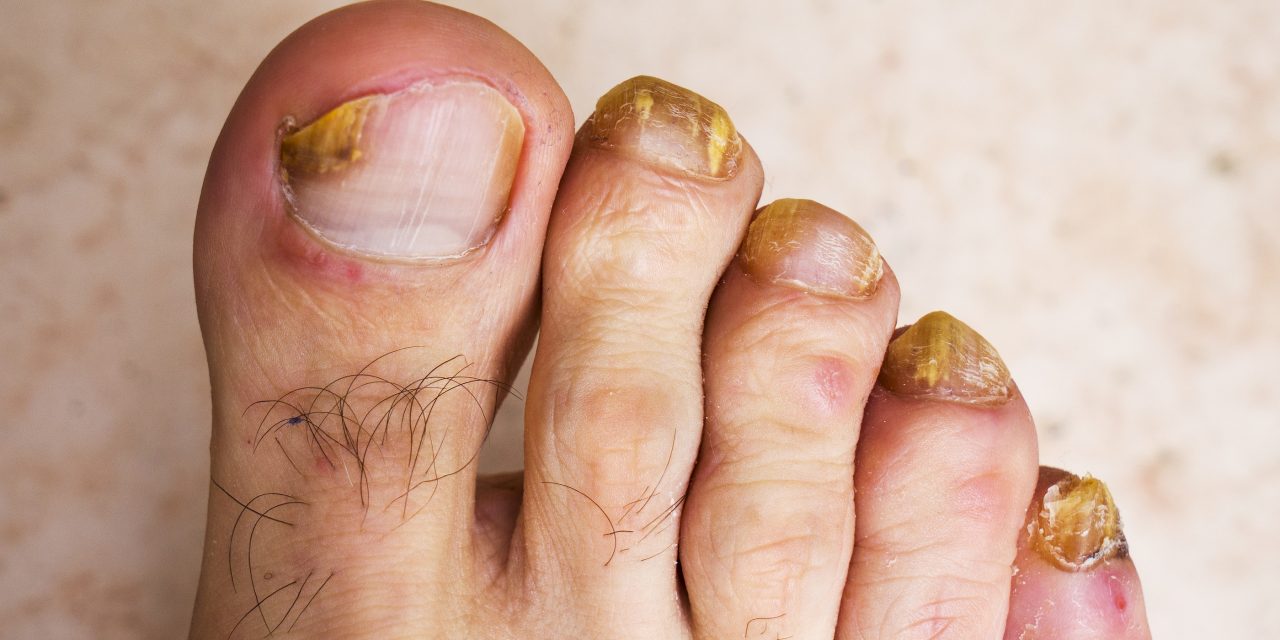
A fungal infection on the toenail typically appears as a white or yellow spot under the tip of the toenail, which may eventually lead to discoloration, thickening, and even crumbling at the edges. This condition might start as a minor discomfort but can cause significant pain and even lead to other health issues if not treated properly.
The appearance of this infection can vary. In some cases, the nails may become dull and lose their shine, while in others, they might thicken and become distorted.
It is crucial to pay attention to any changes in the nails early on, as starting treatment promptly can prevent the infection from worsening and spreading to other nails.
In most situations, identifying the signs of a fungal infection early can make treatment more effective.
Regular cleanliness, proper nail care, and monitoring nail health can help reduce risk. If left untreated, the fungal infections can become resilient and challenging to treat, requiring more advanced interventions.
Key Takeaways
- Toenail fungus appears as discoloration and thickening.
- Early detection can lead to better treatment outcomes.
- Good hygiene and nail care are essential to prevent infections.
Understanding Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, occurs when fungi infect the nails, leading to changes in appearance and texture.
It is important to know the causes and types of toenail fungus for effective prevention and treatment.
Causes of Toenail Fungal Infections
Toenail fungus is often caused by dermatophytes, which are fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments. These fungi can easily spread in public places like swimming pools, showers, and locker rooms where people walk barefoot.
Wearing tight shoes or having sweaty feet can also raise the risk of fungal infection by creating ideal conditions for fungus to grow.
Other fungi, such as yeasts like candida, can cause toenail infections too.
Individuals with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or who suffer from nail injuries may be more susceptible. The use of certain medications or prolonged exposure to water can further increase the risk of developing a fungal infection.
Common Types of Toenail Fungus
There are several common types of toenail fungus.
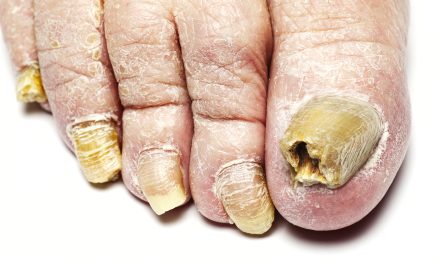
Distal subungual onychomycosis is the most prevalent form, caused mainly by dermatophytes, and typically affects the nail bed and underside of the nail. This type results in a thickened, discolored nail that can become brittle over time.
White superficial onychomycosis is less common and manifests as white patches on the nail surface. It is caused by fungi infecting only the superficial layers of the nail.
Another type, proximal subungual onychomycosis, affects the base of the nail and is more frequent in individuals with a compromised immune system. Understanding these types can help in identifying the infection and seeking the right treatment.
Signs and Symptoms
Toe fungal infections often show specific visual signs. These infections can cause changes in nail appearance, which can help distinguish them from other conditions.
Identifying Nail Infections
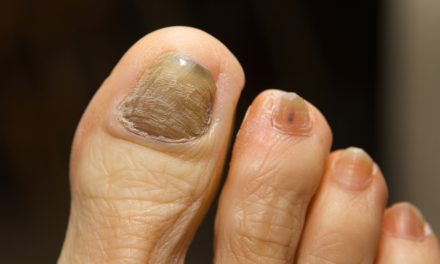
A fungal infection in the toenail often begins with nail discoloration. Affected nails may appear yellow, brown, or white.
Along with color changes, nail thickening is common, making shoes uncomfortable. The texture of the nail may also change, leading to brittle nails or nail crumbling. In some cases, the nail can separate from the nail bed. These symptoms are indicative of conditions like onychomycosis. Early identification is crucial for effective treatment and preventing the spread to other nails.
Comparing Toenail Fungus and Other Conditions
It is important to differentiate fungal infections from other conditions such as psoriasis. Psoriasis can also cause nail discoloration and nail thickening. Unlike fungal infections, psoriasis may be accompanied by red, scaly patches on the skin.
Other skin conditions could mimic the symptoms of a fungal infection. For example, trauma to the nail may cause similar discoloration, but this usually results from a specific injury.
Observing additional symptoms and understanding the cause can help in distinguishing these conditions. Consulting a healthcare professional can provide a definitive diagnosis.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Fungal infections on the toes can be more likely to occur in certain individuals and environments. Understanding key factors like health issues and habits can help prevent their development.
Contributing Health Issues
Individuals with a weak immune system are more susceptible to toe fungal infections. A compromised immune system may struggle to fight off the fungi that cause these infections.
Diabetes is another significant risk factor. People with diabetes often have reduced blood flow to the feet, making it harder for the body to combat infections. This decreased circulation can lead to more prolonged and severe fungal infections.
Conditions like athlete’s foot also contribute. This common foot condition can spread to the toenails, leading to tougher infections. Regular monitoring and care of foot health are important for individuals with these risks.
Minimizing Exposure in Public Places
Public places, particularly wet and moist environments, increase exposure to fungi. Swimming pools, locker rooms, and communal showers are common sources.
Wearing flip-flops or water shoes in these settings can act as a barrier and reduce direct contact with surfaces where fungi thrive.
Ensuring that feet are thoroughly dried after being in damp environments is crucial. Moisture between toes can create a breeding ground for infections.
Regularly changing socks and wearing breathable footwear helps keep feet dry. By taking these preventative measures, individuals can significantly lower their risk of contracting toe fungal infections.
Diagnostic Approaches
Identifying a toe fungal infection requires the right diagnosis methods. It’s crucial to know when to seek professional help and what to expect during an examination by a skin or foot specialist.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
If a person notices that their toenails are thickening, changing color, or becoming brittle, it may be time to consult a healthcare provider. Persistent discomfort or frequent infections are other signs that professional advice is needed. Early intervention can prevent more serious complications.
Those with diabetes or compromised immune systems should be especially vigilant. Fungal infections can pose significant risks for them. In these cases, an early visit to a healthcare provider is essential. Prompt diagnosis ensures appropriate treatment and minimizes potential problems.
What a Podiatrist or Dermatologist Will Do
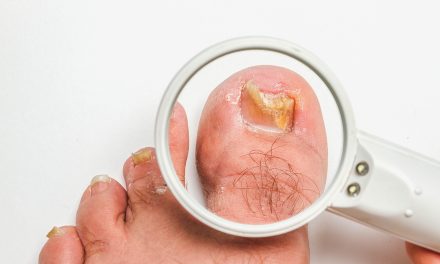
A podiatrist or dermatologist will closely examine the affected toenails. They often use a small tool to scrape off pieces of the nail or skin for laboratory analysis.
This test helps confirm the presence of a fungal infection and identifies the specific fungus involved.
These specialists may also conduct a histological analysis of samples. This process offers further insight into the nature of the infection. With accurate identification, the healthcare provider can then recommend an effective treatment plan tailored to the needs of the patient.
Treatment Options
Toenail fungus can be challenging to treat, but various options are available. Understanding the difference between oral and topical treatments can help determine the best approach. Additionally, some might consider home remedies as alternatives.
Oral vs. Topical Treatments
Oral antifungals, such as terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole, are often used for more severe fungal infections. These medications work by targeting the fungus from within, offering a comprehensive approach that can be effective for tough cases. However, they often require a prescription and can have side effects, such as liver issues or interactions with other medications.
Topical treatments, including medicated nail polish or antifungal creams, are applied directly to the infected area. While they might be less potent than oral medications, they have fewer systemic side effects.
Topicals can be effective when dealing with mild infections or when oral medications aren’t an option.
The Role of Home Remedies
Home remedies are popular for those seeking alternative approaches.
Tea tree oil and apple cider vinegar are commonly used for their antifungal properties. Tea tree oil is applied directly to the nail, while apple cider vinegar is often used in foot soaks.
Essential oils, like oregano or lavender, are also cited for potential benefits, but evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited.
It’s important to note that these remedies may not work for everyone and might be better suited for early-stage or mild infections. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action.
Medications and Their Side Effects
Antifungal medications come in various forms, including oral and topical solutions. Each has its own set of side effects that patients should consider when selecting a treatment.
Commonly Prescribed Antifungal Drugs
Terbinafine and itraconazole are widely used oral antifungal drugs. Terbinafine, often sold under the brand name Lamisil, is effective but can cause liver issues and digestive discomfort. Itraconazole might interact with other medications and can also affect liver function. Physicians typically monitor liver enzymes during treatment.
Efinaconazole and tavaborole are topical medications, often used when oral meds are unsuitable. While generally safer, they may cause localized irritation or redness. Due to fewer systemic side effects, topical treatments are a popular alternative, especially for mild infections.
Over-the-Counter Options
Over-the-counter options include products like ciclopirox nail lacquer. These are topical and typically applied directly to the nail. Ciclopirox may cause mild irritation but is usually well-tolerated. It requires consistent, long-term use to be effective.
Antifungal nail creams and nail-softening creams are other OTC solutions. These often contain agents that help soften the nail for easier application. The main downside is that they demand regular application and may take longer to show results compared to prescription options. Still, they offer an accessible solution for those with mild infections.
Advanced Treatment Techniques
For treating toe fungal infections, advanced approaches like laser therapy and surgical interventions can be significant. Each method offers unique benefits and challenges, making it important to understand their roles in treatment.
Laser Therapy and Its Efficacy
Laser treatment is a promising approach for toe fungal infections. It uses concentrated light beams to penetrate the nail and eradicate the fungus.
This method is non-invasive and can target deep layers of the nail, offering a less painful alternative to other treatments.
The effectiveness of laser treatment can vary. Some studies show positive results, with many patients experiencing significant improvement. There is minimal downtime, and side effects are usually rare. However, multiple sessions might be needed, and effectiveness can depend on the severity of the infection.
Despite these advantages, laser treatment can be expensive. Insurance often does not cover it, which might limit access for some patients.
Those considering this option should consult a healthcare professional to discuss potential results and costs.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention is often considered when traditional treatments fail or when the infection is severe. This process involves removing the infected nail, either partially or completely, to allow a healthy nail to grow back.
One technique is avulsion, where the entire nail is removed. Another is debridement, which removes only part of the infected nail.
These methods can provide relief and improve the effectiveness of topical treatments that are applied afterward.
The recovery time for surgical intervention can vary, but it often results in quicker clearing of the infection. Patients should be aware that like any surgery, there is a risk of pain or infection. Consultation with a specialist is essential to weigh the benefits against these potential risks.
Ongoing Management and Care
Managing toe fungal infections involves daily habits and regular monitoring. Taking care of nails and keeping an eye on progress can prevent the infection from worsening.
Lifestyle and Nail Care
Proper nail care is essential to manage fungal infections. Keeping nails short and clean reduces the risk of spreading the fungus.
Using clean nail clippers is vital. They should be sanitized after every use to prevent further contamination.
Choosing appropriate footwear matters too. Shoes should be breathable and fit well to keep the feet dry.
It’s advisable to avoid walking barefoot in communal areas like gyms or pools, which are common sources of fungi.
Diet can also play a role. Adding biotin supplements can strengthen nails, reducing brittleness and splitting. Avoid sharing personal nail care items as this can spread the infection.
Monitoring and Long-Term Prognosis
Regularly checking the nails helps catch any signs of progress or setbacks. Changes in color, thickness, or shape of the nail plate are indicators of fungal activity.
It’s vital to continue with prescribed nail fungus treatments even after symptoms improve, as this ensures the fungus is fully eradicated.
Different treatment options may be required depending on the severity of the infection. While topical treatments can be effective for minor cases, more severe infections might need oral medications.
Long-term prognosis depends on how consistently the infection is managed. Proper care and maintenance can keep the nail bed healthy and prevent future infections.
Keeping up with routine care is key to avoiding recurring problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Toenail fungal infections can cause various visible changes and discomfort in the nails. Understanding the signs, types, and treatments helps manage the condition effectively.
What are the signs and symptoms of a toenail fungus infection?
A toenail fungus infection often starts with a small white or yellow spot under the tip of the nail. As the infection progresses, the nail may become discolored, thickened, and brittle.
In severe cases, the nail may lift from the nail bed or have a foul odor.
What is the most effective treatment for toenail fungus?
Topical treatments like antifungal creams and ointments can be effective, especially for mild infections. For more severe cases, oral antifungal medications prescribed by a healthcare professional may be necessary.
In some instances, laser treatments or surgical nail removal are considered.
How can you distinguish between toenail fungus and other nail conditions?
Toenail fungus is typically marked by discoloration and thickening, while other conditions like psoriasis might present with pitting or flaking skin around the nail.
It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis since symptoms can overlap.
What are the different types of toenail fungus?
Onychomycosis is the term used for nail fungal infections, and it can be caused by various fungi. The most common types involve dermatophytes, yeasts, and non-dermatophyte molds.
Each type may require a specific treatment approach.
How can you quickly treat a fungal infection on your nails?
Early treatment with over-the-counter antifungal solutions can be effective if started promptly. Keeping the affected area clean and dry is important.
For persistent cases, a healthcare provider can suggest more targeted treatments.
What are the common causes of nail fungus infections?
Fungal nail infections are commonly caused by exposure to moist environments. Walking barefoot in communal areas like swimming pools can also lead to infection. Having a minor skin or nail injury is another common cause. Conditions that impair blood circulation or weaken the immune system can also increase the risk.