Dental implants have become a popular solution for replacing missing teeth, with titanium being the most common material used.
While titanium is known for its durability and biocompatibility, some people may wonder if they could be allergic to it.
Titanium allergies are very rare, affecting less than 1% of patients who receive dental implants.
Symptoms of a titanium allergy can vary. They may include loosening of the implants, rash, or swelling in the mouth.
If you suspect an allergy, it’s crucial to consult your dentist. They can perform tests to determine if you’re allergic to titanium.
For those concerned about potential allergies, there are alternative materials available for dental implants.
Ceramic implants, for example, can be a good option for patients who prefer metal-free solutions or have concerns about titanium sensitivity.
Key Takeaways
- Titanium allergies in dental implants are extremely uncommon.
- Symptoms of titanium allergy can include implant loosening and oral swelling.
- Alternative materials like ceramic are available for those with titanium concerns.
Understanding Titanium Dental Implants
Titanium dental implants are a popular choice for replacing missing teeth. They offer durability and compatibility with the human body. Let’s explore the key aspects of these implants.
Components and Types of Titanium Implants
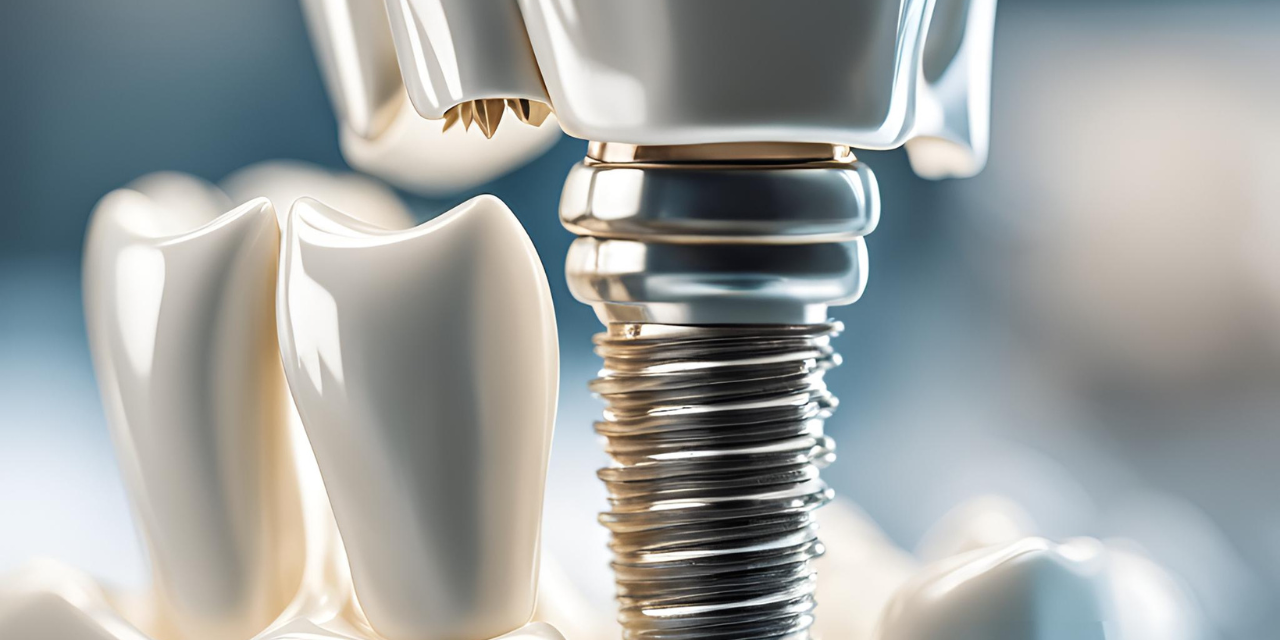
Titanium dental implants have three main parts: the implant, abutment, and crown.
The implant is a screw-like post that goes into the jawbone. The abutment connects the implant to the crown. The crown is the visible part that looks like a real tooth.
There are two main types of titanium implants:
- Endosteal implants: These go directly into the jawbone.
- Subperiosteal implants: These sit on top of the bone but under the gum.
Most implants are made of pure titanium or titanium alloys. These materials are strong and resist corrosion.
The Role of Titanium in Osseointegration
Osseointegration is key to the success of dental implants. It’s the process where bone grows around the implant, securing it in place.
Titanium is great for this because it’s biocompatible.
When placed in the jaw, titanium forms a thin oxide layer. This layer helps the bone attach to the implant.
Over time, new bone cells grow and connect with the implant surface.
The osseointegration process can take several months. During this time, the implant becomes a strong anchor for the new tooth.
Pros and Cons of Titanium Dental Implants
Titanium implants have many benefits:
- Long-lasting and durable
- High success rate
- Look and feel like natural teeth
- Help maintain jawbone health
- Allow normal eating and speaking
But there are some drawbacks to consider:
- Allergic reactions in rare cases
- High initial cost
- Require surgery
- Need several months to heal fully
It’s important to discuss these points with a dentist before deciding on titanium implants. They can help determine if implants are the right choice for each patient’s needs.
Allergy to Titanium: Incidence and Causes
Titanium allergies are rare but can occur in some people. The immune system may react to titanium particles, causing various symptoms.
Immunological Response to Titanium
The body can sometimes view titanium as a foreign substance. This triggers an immune response. When this happens, the person experiences allergic reactions to titanium.
Symptoms may include:
- Skin rashes
- Inflammation
- Pain near the implant site
- Loosening of the implant
In severe cases, the immune system’s reaction can lead to implant failure. Immunohistochemical analysis of affected tissues shows increased presence of inflammatory cells.
Identifying Risk Factors for Titanium Allergy
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing a titanium allergy.
People with existing metal allergies are more likely to react to titanium.
Other risk factors include:
- Genetic predisposition
- Previous exposure to titanium
- Compromised immune system
Doctors can use patch tests to check for titanium sensitivity before implant surgery.
Blood tests may also help identify potential hypersensitivity to titanium.
Patients should inform their dentist about any known metal allergies. This helps in choosing the most suitable implant material.
Clinical Manifestations of Titanium Allergies
Titanium allergies can cause a range of symptoms that affect both the oral cavity and other parts of the body. These reactions may appear soon after implant placement or develop over time.
Early and Late Stage Allergic Symptoms
Early signs of titanium allergy often occur within days or weeks of implant surgery.
Patients may experience redness, swelling, and pain around the implant site. Some people report a burning sensation or metallic taste in their mouth.
Late stage symptoms can develop months or even years after implantation. These may include:
- Persistent pain or discomfort
- Loosening of the implant
- Gum recession
- Chronic inflammation of surrounding tissues
- Peri-implantitis, an inflammatory condition affecting the gums and bone around the implant
In severe cases, patients might experience systemic symptoms like skin rashes, fatigue, or muscle pain.
Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosing a titanium allergy can be challenging as symptoms often mimic other dental issues. Dentists must rule out:
- Infection
- Poor oral hygiene
- Improper implant placement
- Other metal allergies
Patch testing can help identify titanium sensitivity.
Blood tests may also be used to detect titanium-specific antibodies.
Imaging techniques like X-rays or CT scans can reveal bone loss or necrosis around the implant. These signs, combined with clinical symptoms, help differentiate titanium allergies from other conditions.
Diagnostic Methods for Titanium Sensitivity
Doctors use different tests to check if someone has a titanium allergy. These tests look at how a person’s body reacts to titanium. Some tests use blood samples, while others involve putting small amounts of metal on the skin.
Laboratory Tests for Metal Allergy Detection
The MELISA test is a key lab test for metal allergies. It checks how white blood cells react to titanium.
Doctors take a blood sample and mix it with titanium. If the cells react strongly, it may mean an allergy.
Another test is the lymphocyte transformation test. This also uses blood samples. It measures if certain blood cells grow when exposed to titanium. A big increase in cell growth can point to an allergy.
These lab tests are helpful because they don’t put titanium directly on the skin. This makes them safer for people who might have strong allergies.
Skin Testing and Immunological Assays
Skin tests are another way to check for titanium allergies. The patch test is common.
A doctor puts a small amount of titanium on the skin. They cover it and check for a reaction after a few days.
Some doctors use blood tests that look at antibodies. These tests check if the body has made special proteins to fight titanium.
A high level of these proteins might mean an allergy.
Skin tests are good because they show real skin reactions. But they can sometimes cause discomfort.
Blood tests are often safer but may not catch all allergies.
Oral Health Implications and Implant Failure
Titanium allergies can affect oral health and implant success. These issues may lead to complications and potential implant failure if not addressed properly.
Impact of Titanium Allergy on Oral Tissues
Titanium allergies can cause various reactions in oral tissues.
Swelling, pain, and eczema may occur in the gums around the implant. In some cases, patients experience necrosis, which is the death of cells or tissue near the implant site.
Peri-implant disease can develop as a result of titanium allergies. This condition causes inflammation and infection in the tissues surrounding the implant. If left untreated, it may progress to bone loss.
Bone loss around implants is a serious concern. Studies have shown higher levels of titanium in the lungs and lymph nodes of patients with failed implants compared to successful cases.
Preventing and Managing Implant Failures
Early detection of titanium allergies is crucial for preventing implant failure. Dentists may recommend allergy tests before implant placement to identify at-risk patients.
For those with confirmed allergies, alternative materials like zirconia implants can be considered. These non-metal implants may reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
Regular check-ups and proper oral hygiene are essential for managing implant health. Patients should report any unusual symptoms promptly to their dentist.
Radiographic follow-ups are important for monitoring bone levels and implant integration.
If problems arise, early intervention can help prevent complete implant failure and preserve oral health.
Alternatives to Titanium Implants
For people with titanium allergies or concerns, other dental implant options exist. These alternatives offer similar benefits while avoiding potential metal sensitivities.
Zirconia Implants: A Viable Option
Zirconia implants are gaining popularity as a metal-free alternative to titanium. Made from a strong ceramic material, they offer several advantages:
• Highly biocompatible
• White color that blends with natural teeth
• Resistant to corrosion and wear
Zirconia implants are especially good for patients with metal allergies or sensitivities. They don’t trigger allergic reactions and integrate well with bone tissue.
These implants also have aesthetic benefits. Their white color looks more natural, especially in areas where the implant might be visible.
Comparing Titanium and Non-Metallic Implant Materials
When choosing between titanium and non-metallic implants, several factors come into play:
- Durability: Titanium implants have a long track record of durability. Zirconia implants are newer but show promising long-term results.
- Allergic reactions: Zirconia implants are hypoallergenic, making them ideal for patients with metal sensitivities.
- Aesthetics: Ceramic implants offer a more natural look, especially in patients with thin gums.
- Cost: Zirconia implants are often more expensive than titanium due to newer technology and less widespread use.
Both options have pros and cons. The best choice depends on individual patient needs, allergies, and aesthetic preferences.
The Biocompatibility of Dental Materials
Dental materials must be safe for long-term use in the mouth. Two key factors are how well they resist breaking down and whether they cause allergic reactions.
Corrosion Resistance and Allergy Potential
Dental implants need to withstand the harsh environment in the mouth. Titanium is widely used because it resists corrosion well.
This means it doesn’t easily break down when exposed to saliva and foods. But some people may be allergic to titanium.
This can cause problems like pain or implant failure. Allergic reactions are rare but possible.
Other metals used in implants can also corrode over time. This may release particles that irritate the surrounding tissues.
Dentists try to choose materials that are both strong and unlikely to cause reactions.
Advances in Dental Material Sciences
Scientists keep working to make dental materials better. New coatings can help implants bond with bone faster. This speeds up healing after surgery.
Some new materials release helpful substances. These can fight bacteria or encourage bone growth. Zirconia is an alternative to titanium that some people prefer.
Researchers study how different materials affect the body. They look at things like inflammation and cell growth. The goal is to find materials that work well and don’t cause problems.
Testing for metal allergies before getting implants may become more common. This could help prevent issues for people who are sensitive to certain metals.
Evidence-Based Research on Titanium Implant Allergies
Research on titanium implant allergies has grown in recent years. Studies have looked at both case reports and larger reviews to understand this issue better.
Analysis of Clinical Case Reports and Reviews
Clinical case reports have shed light on titanium implant allergies. These reports show that some patients develop symptoms after getting titanium implants.
Common signs include skin rashes, pain, and swelling near the implant site. In vitro studies have also been helpful.
They test how human cells react to titanium in lab conditions. These studies suggest that some people’s immune systems may overreact to titanium particles.
Clinical studies have tracked patients over time. They’ve found that titanium allergy symptoms can appear weeks or even years after implant placement.
Outcomes from Scoping and Systematic Reviews
A scoping review looked at many studies on titanium allergies. It found that allergic reactions to titanium implants are rare but possible. The review noted that failed implants had higher amounts of titanium in nearby tissues.
A systematic review focused on dental implants specifically. It showed that patients with metal allergies might be more likely to react to titanium. The review also pointed out that better testing methods are needed to diagnose titanium allergies accurately.
These reviews stress the need for more research. They suggest that doctors should consider titanium allergies when implants fail without clear reasons.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Dental implants are subject to strict regulations and legal standards. These rules aim to protect patients and ensure ethical practices in dentistry.
Regulatory Standards for Dental Implants
The FDA sets guidelines for dental implant materials and procedures. Titanium implants must meet specific safety and quality standards before approval for use in patients.
Manufacturers have to prove their implants are safe and effective. This involves extensive testing and clinical trials.
Regular inspections of production facilities help maintain quality control. The FDA can recall implants if safety issues arise after approval.
Dentists must follow strict protocols when placing implants. This includes proper sterilization and adherence to surgical best practices.
Patient Informed Consent and Ethical Practice
Dentists are legally required to obtain informed consent from patients before implant surgery. This means explaining the procedure, risks, and alternatives.
Patients should be told about the possibility of titanium allergies, even though they are rare. Dentists must discuss potential complications and success rates.
Ethical practice involves recommending implants only when medically necessary. Dentists should not push unnecessary procedures for financial gain.
Patients have the right to access their dental records and seek second opinions. Clear communication about costs and insurance coverage is also essential.
Communicating with Your Dental Professional
Open and honest communication with your dentist is key when dealing with potential titanium implant allergies. Your dental professional can guide you through the process of diagnosis and treatment options.
Discussing Concerns and Symptoms with Your Dentist
If you suspect a titanium allergy, schedule an appointment with your dentist. Be prepared to describe any symptoms you’re experiencing, such as:
• Persistent pain or discomfort
• Swelling or inflammation
• Rashes or hives
• Loosening of the implant
Provide a detailed timeline of when symptoms started and how they’ve progressed. Your dentist may ask about your medical history and any known allergies.
Be ready to answer questions about medications you’re taking and lifestyle factors that might affect implant success. This information helps your dental professional develop a clear picture of your situation.
Navigating Treatment Options and Decisions
Your dentist will explain the diagnostic tests available to confirm a titanium allergy. These may include patch tests or blood tests to check for metal sensitivities.
If an allergy is confirmed, discuss alternative implant materials with your dentist. Ceramic implants are a popular option for those with metal sensitivities.
Ask about the pros and cons of each treatment option. Consider factors like durability, cost, and long-term success rates. Your dentist can provide insight into which choice might work best for your specific case.
Don’t hesitate to seek a second opinion if you’re unsure about the recommended treatment plan. It’s important to feel confident in your decision regarding dental implants.
Conclusion
Titanium dental implants can cause allergic reactions in some people. While rare, these reactions can impact a patient’s health and well-being.
Common titanium allergy symptoms include:
• Skin redness
• Hives
• Eczema
• Swelling
• Pain
Patients with allergies to other metals may be more likely to react to titanium implants.
Doctors can use patch tests or blood tests to check for titanium sensitivity. If an allergy is confirmed, alternative materials like zirconia may be used for implants.
For those experiencing symptoms, removal of the implant is often necessary. This can improve quality of life for affected patients.
Research on titanium allergies continues to evolve. New testing methods and treatment options may emerge to better help patients in the future.
Individuals concerned about potential allergies should discuss their medical history with their dentist before getting implants. Careful screening can help prevent adverse reactions and ensure positive outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Titanium dental implants can sometimes cause allergic reactions. These questions address common concerns about symptoms, diagnosis, and management of titanium allergies.
What are the common signs indicating a titanium implant allergy?
Signs of a titanium implant allergy may include redness, swelling, or pain around the implant site. Some patients report itching, rashes, or a burning sensation in the mouth.
Unexplained fatigue or general discomfort can also occur. In rare cases, more severe symptoms like fever or difficulty breathing may develop.
What methods are available for diagnosing titanium allergy in dental implant patients?
Doctors use several tests to diagnose titanium allergies. Blood tests can check for immune system reactions to titanium.
Patch tests involve applying small amounts of titanium to the skin to see if a reaction occurs. Some clinics offer specialized tests that measure cellular responses to titanium.
Is it possible to have an allergic reaction to titanium-based jewelry?
Yes, people can have allergic reactions to titanium jewelry. Symptoms may include skin redness, itching, or rashes where the jewelry touches the skin.
These reactions are less common with titanium than with other metals. Pure titanium rarely causes issues, but some titanium alloys may contain other metals that trigger reactions.
Are there any reported side effects associated with titanium screws used in medical procedures?
Titanium screws in medical procedures can cause side effects in some patients. Pain, swelling, or infection at the screw site may occur.
Rarely, patients report systemic symptoms like fatigue or skin problems. In most cases, titanium screws are well-tolerated and cause few issues.
How prevalent is titanium allergy among individuals with dental or orthopedic implants?
Titanium allergies are rare in dental and orthopedic implant patients. Studies estimate that less than 1% of people have titanium sensitivity.
However, the exact prevalence is hard to determine. Some cases may go undiagnosed or be mistaken for other issues.
What steps should one take if they suspect their body is rejecting a titanium implant?
If rejection is suspected, patients should contact their dentist or doctor immediately. The healthcare provider will examine the implant site and may order tests.
Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms. Options range from medication to manage symptoms to removing the implant in severe cases.